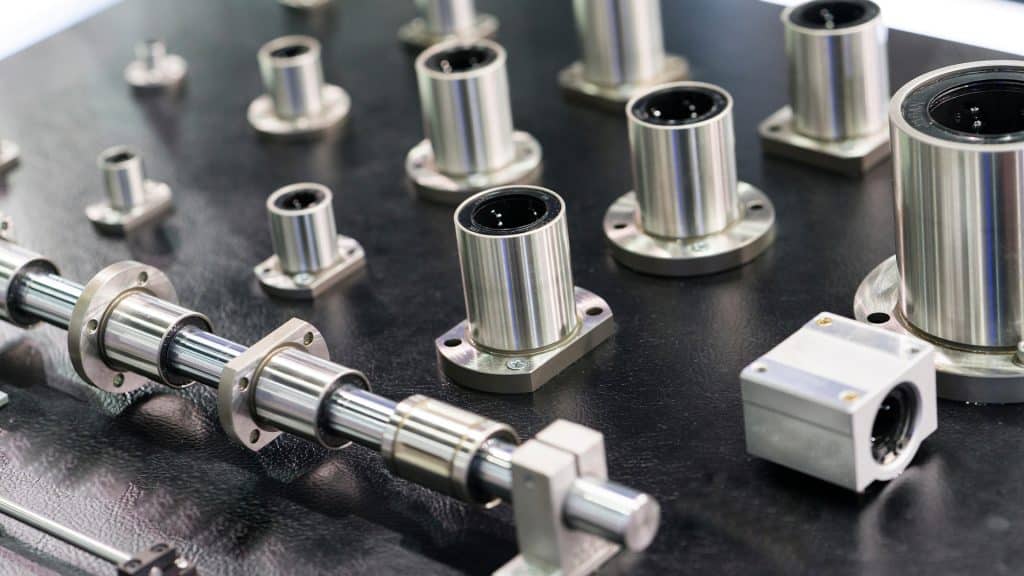
Use a flanged bushing when you need radial + moderate axial in a compact part. For high axial or serviceable stacks, a separate thrust washer is easier to replace and size.
What Are Thrust & Flanged Bushings?
Thrust bushings (thrust washers) carry axial load between faces.
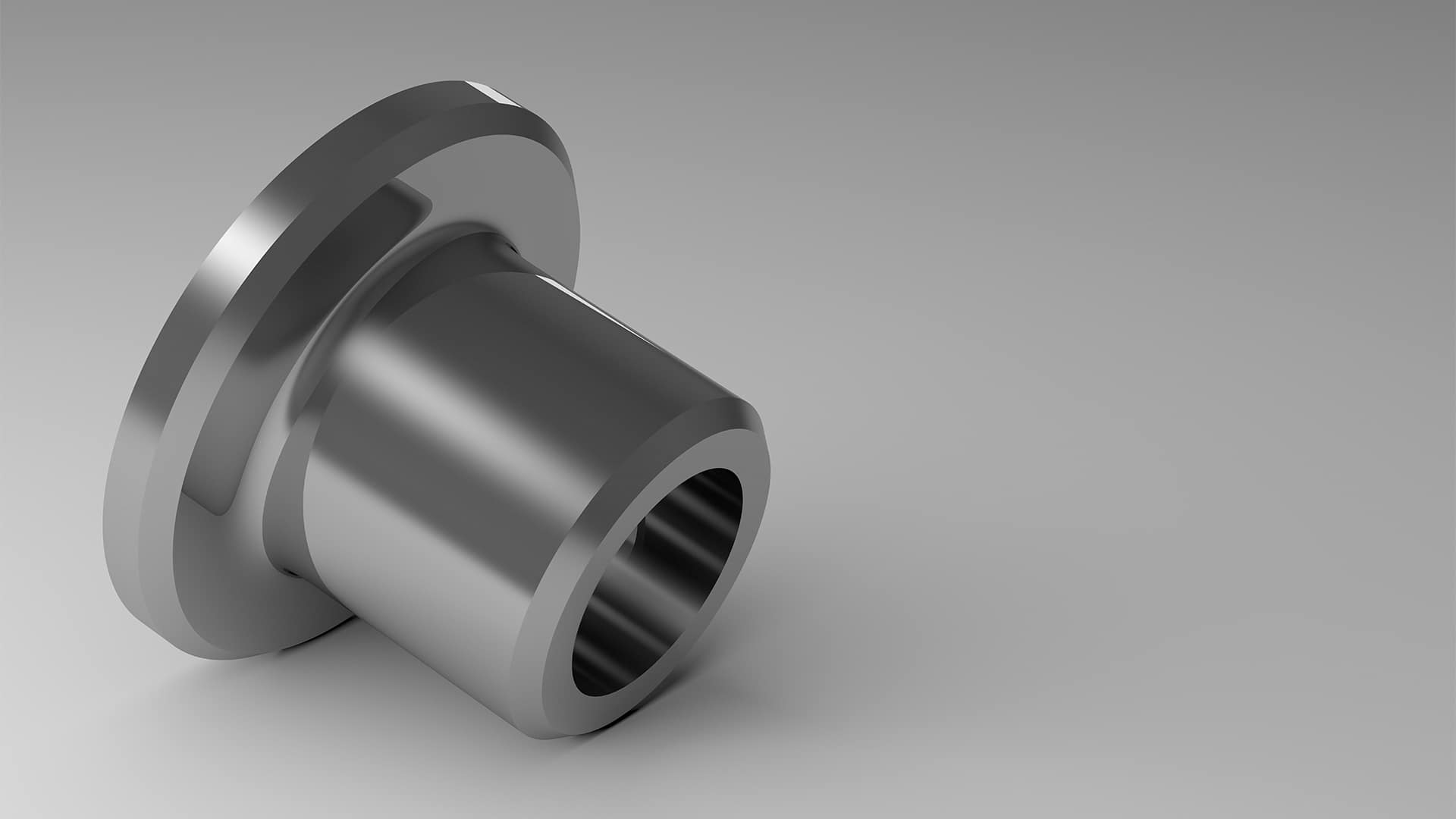
Flanged bushings are sleeve bushings with an integral flange that locates the bushing and/or
shares axial load while the cylindrical ID still supports radial load on the shaft.
They run in boundary/mixed lubrication much of the time; life depends on PV, materials, clearance, and surface finish.
Typical uses: linkages with end thrust, stop faces, indexing tables, actuators with axial reaction,
hinges and door mechanisms, conveyors (end thrust), packaging & food equipment (washdown), marine and outdoor hardware.
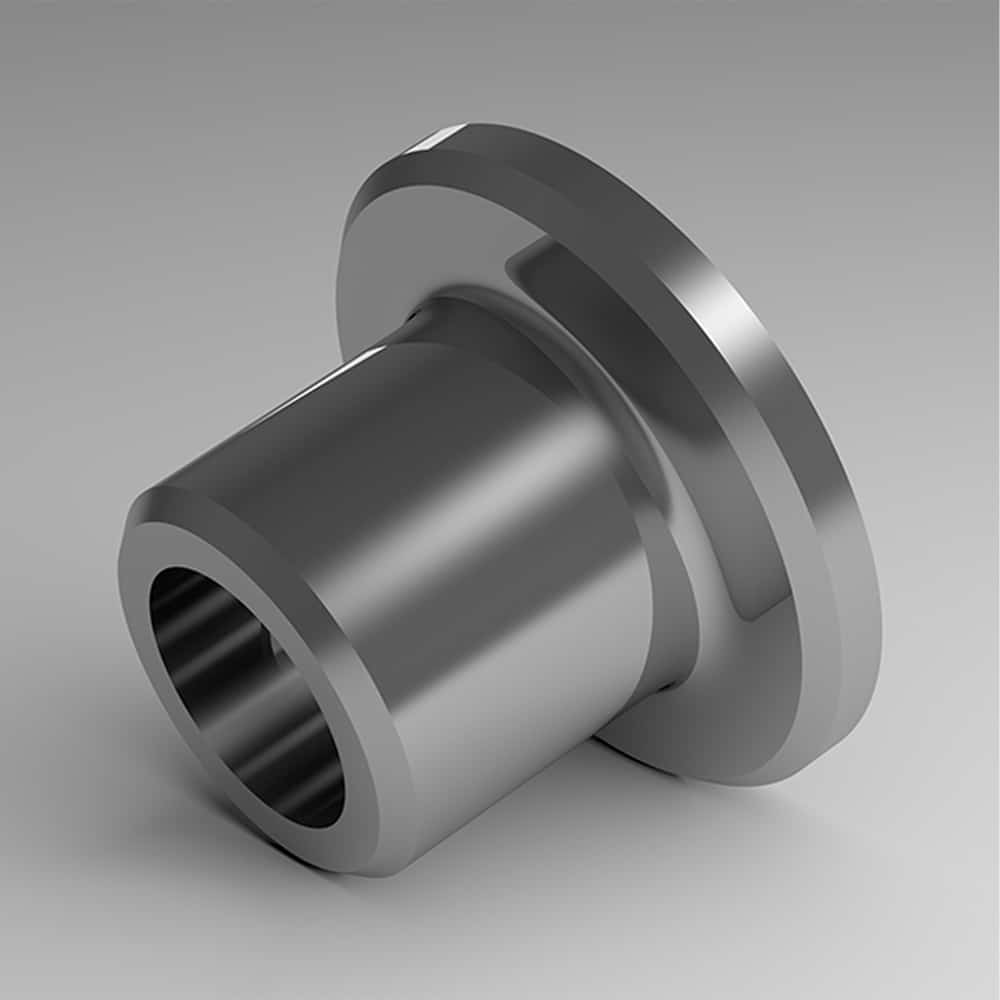

Selection Cheatsheet (Duty, PV, Geometry, Environment)
- Mostly axial load? Thrust washer or flanged bushing with adequate flange area; verify face pressure and torque.
- Combined load? Flanged bushing handles radial via ID and axial at flange; confirm both PV (ID) and face pressure (flange).
- Oscillation/start-stop? Favor PTFE/composite liners or polymers tuned for boundary regime.
- Sustained rotation? Use oil feed and groove pattern that doesn’t starve the loaded arc; consider bronze/babbitt.
- Environment drives materials: washdown → stainless + inert coatings; abrasive → hard low-roughness surfaces + seals.
- After coatings: re-measure ID/OD, flange thickness & flatness, face runout, and hot clearance.
Environment → Attributes Matrix
| Environment | Material / Surface | Clearance / Flatness | Fits (shaft / housing) | Sealing | Lubrication |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Oscillating hinge with end thrust | PTFE/composite liner; hard chrome on pin & flange face | Nominal clearance; flange flatness critical for smooth torque | Pin h6–h9 / Housing H7 with OD interference to prevent spin | Deflectors or boots | Grease purge schedule; compatible with liner |
| Indexing table axial stop | Bronze/babbitt thrust washer; ground face; optional chrome | Face flatness/parallelism; runout <= torque spec | Clamped stack; anti-rotation features | Non-contact shields; chip guards | Oil feed or high-quality grease for stop impacts |
| Washdown / Food | Stainless shells; inert chrome or Ni-P on faces & pins | C3-like looseness concept if thermal rise; verify torque hot | k5–m6 / H7; confirm post-coat ID & flange thickness | Contact seals + deflectors; avoid jets at faces | H1 grease; purge after wash; dry-out routine |
| Dusty / Abrasive | Hard, low-roughness shaft & face coatings; wear-tolerant liners | Don’t over-tighten; allow film | Secure fits; add anti-rotation notch if needed | Labyrinth + shields; purge paths | Grease with sealing behavior; set purge interval |
| High temperature | High-temp polymers/composites or bronze/babbitt | Clearance for thermal growth; face flatness maintained hot | Thermal growth model for fits/clamp | Heat shields / non-contact seals | High VI oil or dry-film compatible liner |
Common Failures & Diagnostics
Rapid Triage
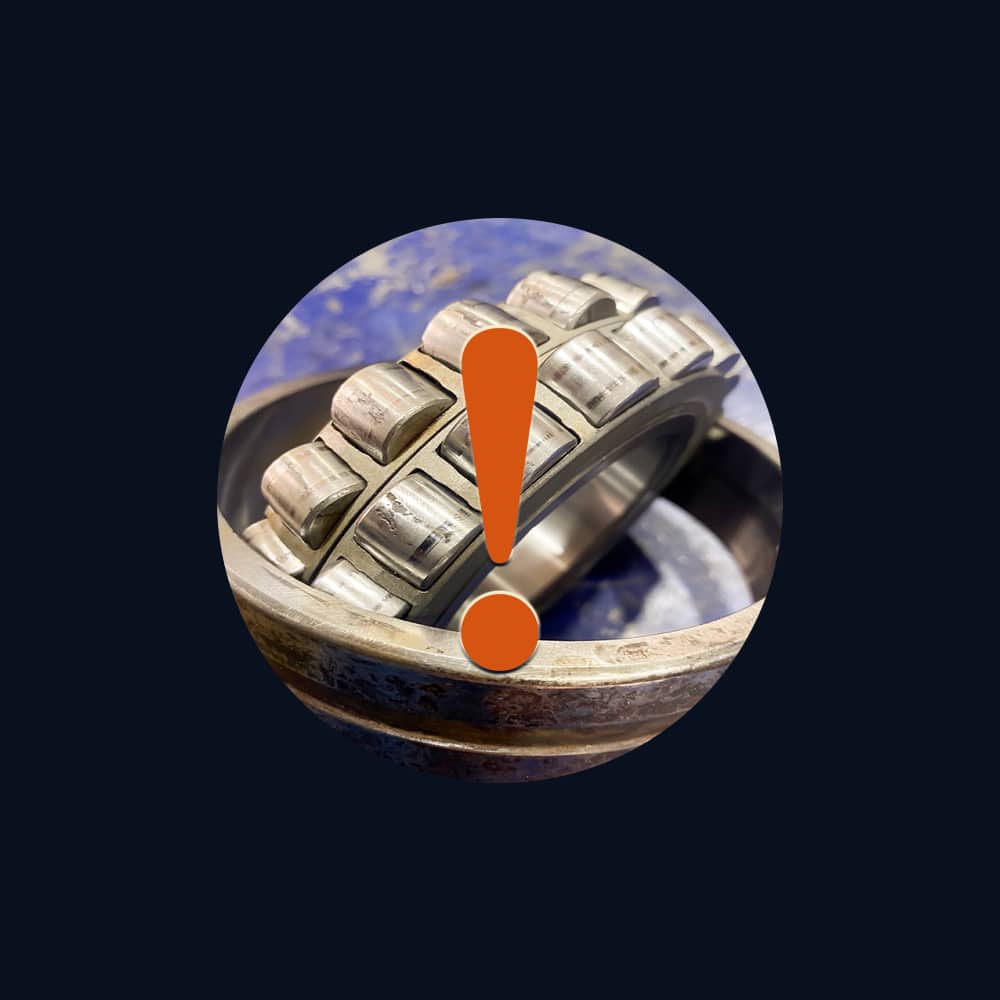

1) Thrust Face Wear / Grooving
Symptoms
Rising axial play, scratch rings on face, torque fluctuations.
Likely causes
Abrasive ingress, PV over limit, inadequate lubrication, face not flat/parallel.
Checks
Face flatness & runout; contamination paths; PV vs. catalog; groove design.
Non-coating actions
Improve sealing/guards; adjust grease/oil; redesign grooves; reduce load or speed.
When surface treatments help
Hard, low-roughness chrome on face reduces abrasion once ingress is controlled.
2) Seizure / Scoring (ID or face)
Symptoms
Squeal, heat spike, visible scoring on shaft or face.
Likely causes
Clearance too tight hot, viscosity too low, misalignment, overload.
Checks
Hot clearance; viscosity @ temp; face parallelism; alignment.
Non-coating actions
Resize clearance; raise viscosity/cooling; correct alignment; add grooves.
When surface treatments help
Low-roughness chrome reduces adhesion after clearance/lube are correct.
3) Fretting at Flange Seat / OD
Symptoms
Reddish oxide at OD or under flange, creak/squeak, micro-motion marks.
Likely causes
Insufficient interference or clamp; vibration; thermal cycles.
Checks
Fit classes; clamp torque sequence; seat finish; transport profile.
Non-coating actions
Increase interference/anti-rotation features; improve clamp and seat flatness.
When surface treatments help
Micro-textured chrome on seats lowers adhesion once fits are corrected.
4) Flange Cupping / Extrusion
Symptoms
Edge-high contact, uneven wear ring, flange deformation.
Likely causes
Face not supported; clamp over-torque; thermal gradients; polymer creep.
Checks
Seat flatness; clamp distribution; temperature map; material choice.
Non-coating actions
Improve backing washer/seat; adjust clamp; choose stiffer material.
When surface treatments help
Not primary; geometry/support dominates.
5) Stick-Slip / High Breakaway Torque
Symptoms
Jerky axial starts, audible squeak, inconsistent positioning.
Likely causes
Boundary regime with high μs/μk; incompatible grease; rough faces.
Checks
Grease chemistry; face finish; temperature; groove pattern.
Non-coating actions
Change grease; polish faces; adjust preload or dwell profile.
When surface treatments help
Low-roughness chrome reduces μ variance after lube/grooves are corrected.
The Big Three: Corrosion, Lubricity, Dimensional Stability
Use coatings when they address surface-driven issues (corrosion, fretting, abrasion) on pins/shafts, faces, and housing seats. Coatings don’t replace clearance control, alignment, sealing, or lubricant choice.
| Concern | What it means | Non-coating controls (first) | When coatings help | Notes |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Corrosion resistance | Protect faces, IDs/ODs, and pins from rust/chemicals | Seals/deflectors; wash angles; drying; compatible H1 grease | Thin dense/micro-cracked chrome or Ni-P on faces & pins | Re-measure ID and face flatness after processing |
| Lubricity | Reduce stick-slip under axial load and oscillation | Right grease/oil; groove design; PV within material limits | Low-roughness/micro-textured chrome on pins & faces | Coatings complement—don’t replace lubrication discipline |
| Dimensional stability | Keep clearance, flange thickness, and face runout in spec | Thermal model; rigid seats; correct clamp sequence | Controlled-thickness coatings; post-coat metrology | Small thickness shifts change torque & axial play |
Fits, Geometry & Axial Location (Quick Rules)
-
Pin/shaft fit: sliding fit for motion (e.g., h6–h9 vs. bushing ID). Finish Ra ≤ ~0.2–0.4 μm for liners.
-
OD/seat: prevent spin/fretting—use interference or anti-rotation features; seat flatness matters under the flange.
-
Flange face: perpendicular to bore; adequate thickness; support with a flat backing surface to avoid cupping.
-
Grooves & chamfers: add grease/oil pockets without starving loaded arc; chamfers clear shaft radii.
-
After coatings/linings: ream/hone to size; re-measure ID, flange thickness, face runout, and hot clearance.
Checklist
-
Seat flatness/parallelism verified
-
Hot clearance modeled/checked
-
Face runout & torque within spec
-
Post-process metrology complete
Frequently Asked Questions
Within its face area and material PV limit—verify face pressure and torque. For heavy axial duty, consider a dedicated thrust washer/bearing.
Only liners designed for dry running should run dry. Bronze/babbitt needs grease/oil; polymers vary—check the catalog.
Yes. Control thickness, then ream/hone IDs and re-measure flange thickness and face runout after coating.
Use proper OD interference, knurls/serrations, flats, or anti-rotation tabs; confirm clamp sequence.
Case Snapshots
- Indexing stop face wear — Bronze thrust washer grooved after packaging dust ingress.
Actions: added deflectors, switched to micro-textured hard chrome face + filtered oil feed; verified runout.
Outcome: torque stabilized; no new grooves after 6 weeks. - Washdown hinge stick-slip — PTFE-lined flanged bush squealed after sanitation cycles.
Actions: hard-chrome pins + H1 grease purge; added boots; validated cleaner pH; rechecked flange flatness.
Outcome: smooth start torque; reduced staining through audit period.
Have a failure photo, sound clip, or spec?
Upload it for a no‑fluff diagnostic checklist. We’ll map symptoms → checks → next actions (and only propose coatings when they’re truly indicated).