When stiffness/deflection under load is the limiter (machining/grinding, heavy tooling, tall gantries). Roller line contact gives higher rigidity at similar envelope.
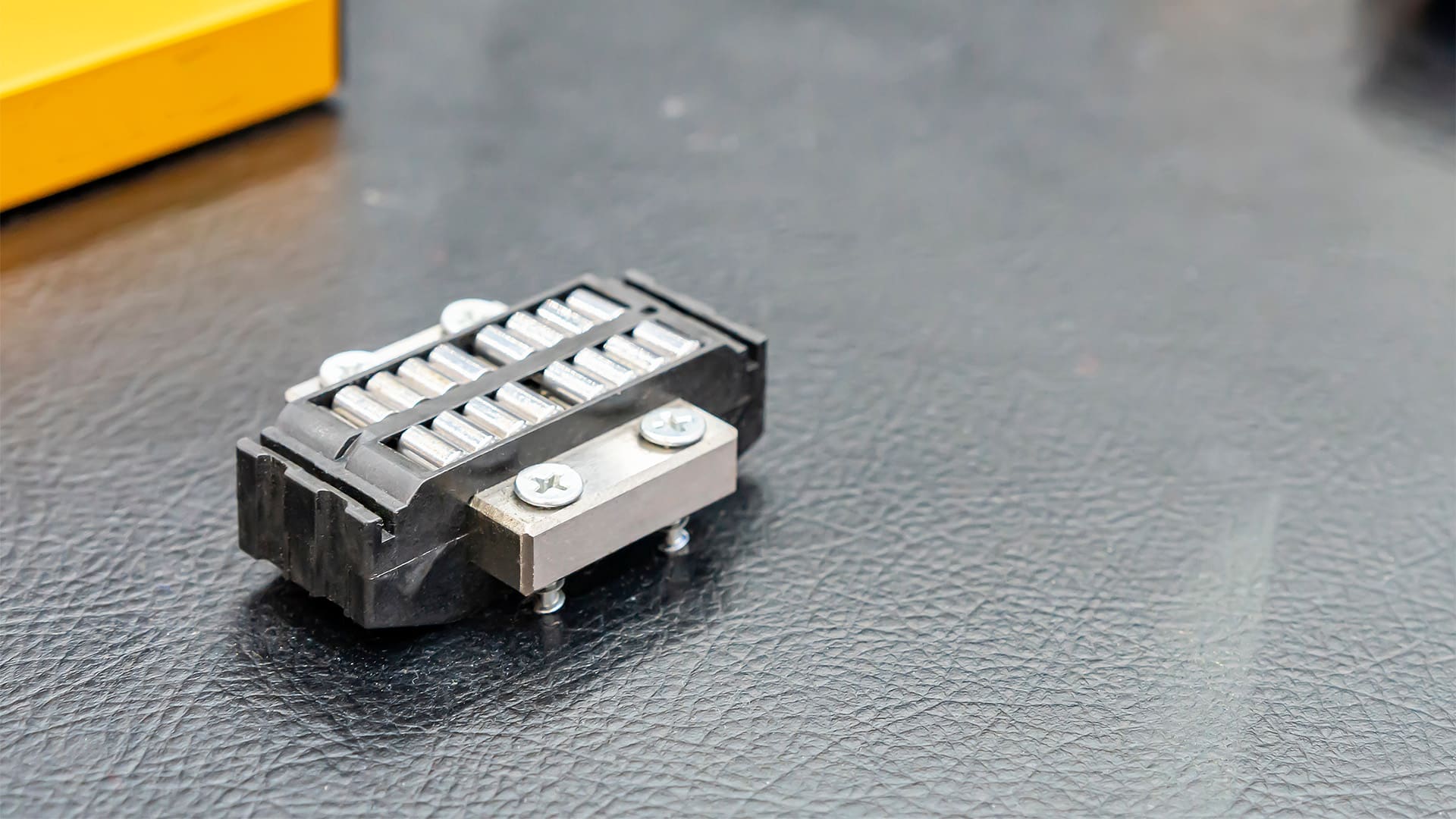
Profile Rail — Recirculating Roller Guides
Linear guideway with recirculating cylindrical rollers for line contact stiffness and very high load capacity. Excels under cutting forces, heavy tooling, and precision gantries where deflection must be minimal.
Typical uses: CNC machining centers, grinding machines, battery/EV lines, heavy pick-and-place, precision press feeds, large CMM/gantry axes.
Selecting Your Roller Profile Rail
Choose carriage geometry, preload, sealing, and rail strategy to balance stiffness, drag, and contamination control.
| Choice | Use when | Watch-outs | Notes |
|---|---|---|---|
| Carriage: Short / Std / Long / Wide | Wide/Long raises moment stiffness for cutting/grinding loads. | Added drag & cost; requires better base flatness to avoid binding. | Two carriages per rail, spaced, dramatically boost pitch/yaw. |
| Preload: Light / Medium / Heavy | Medium for metal-cutting; heavy only on sealed/clean systems. | High preload ↑ heat/torque; amplifies misalignment effects. | Torque-map after assembly to locate tight spots. |
| Sealing: Wipers / Scrapers / Bottom seals | Scrapers for chips/coolant; bottom seals for side/inverted mounts. | More contact → more drag; check motor sizing & heat. | Pair with bellows/way covers in aggressive chip spray. |
| Material/finish: Std / Stainless / Coated | Coated/stainless for corrosives or coolant; heavy washdown. | Micron-level height change; re-map after coating. | Plug rail holes; deflectors at carriage ends. |
| Rail strategy: Fixed + Floating | Long axes; temperature swings; mixed materials. | Both rails fixed → thermal bind; joint steps add ripple. | Index master rail first; shim slave to torque curve. |
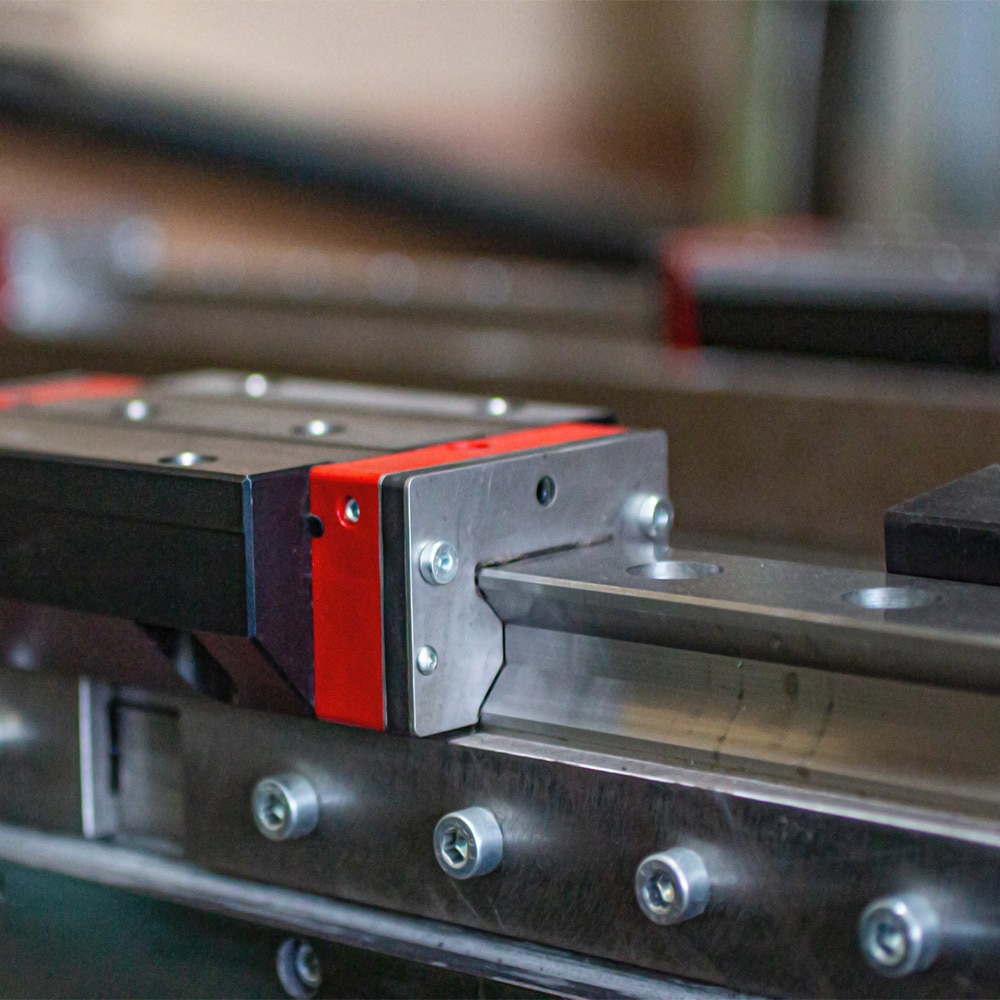
Mounting & Design Rules (Roller Rails)
-
Datum first: Align “master” rail; shim “slave” rail by torque mapping along travel.
-
Flatness/parallelism: Line contact is unforgiving—verify pad quality and joint steps.
-
Thermal growth: Use fixed+floating; avoid clamping both rails solid on long axes.
-
Post-coat checks: Re-map height/straightness and verify preload/drag after coating.
Environment → Recommended Attributes (Roller Rails)
| Environment | Rail/Carriage Options | Sealing/Covers | Lube | Notes |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CNC chips + coolant | Long/wide blocks; high stiffness class | Metal scrapers + double-lip; full covers/bellows | Oil metering; coolant-compatible oils | Keep recirculation paths shielded; cap rail holes |
| Heavy automation | Std/long blocks; medium preload | Wipers + deflectors; light covers | Grease or oil; set purge interval | Monitor torque drift as a health metric |
| Washdown / corrosive | Stainless/coated rails; corrosion-tolerant blocks | Double-lip seals; deflectors; avoid direct jets at lips | NSF H1 grease or compatible oil; drying routine | Validate against cleaner pH; re-map height after coating |
| Precision gantry / metrology | High accuracy class; light preload to limit force ripple | Non-contact shields + clean covers | Low-bleed grease or light oil | Cable management to minimize parasitic forces |
Common Failures & Diagnostics

1) Debris Denting → Rough Motion / Torque Ripple
Symptoms
Clicking at repeat locations, chatter marks, rising drag.
Likely causes
Chips/slurry bypassing wipers; inadequate scrapers/covers.
Checks
Seal wear; debris behind scraper; oil path condition.
Non-coating actions
Upgrade to scrapers + bellows; set purge and chip extraction.
When surface treatments help
Hard, low-Ra coatings resist fretting/oxidation on rails.
2) Heat Build from Over-Preload / Lube Starvation
Symptoms
Hot carriages, burnt grease odor, speed limits dropping.
Likely causes
Preload too high; oil feed restricted; high seal drag.
Checks
Torque map vs. position; temperature scan; verify flow.
Non-coating actions
Reduce preload; switch to oil metering; low-drag seals where feasible.
When surface treatments help
Secondary—fix mechanics and lubrication first.
3) Corrosion After Idle / Coolant Attack
Symptoms
Brown staining at ends, noisy restart, pitting along race.
Likely causes
Aggressive coolant/cleaners; poor drying; incompatible grease.
Non-coating actions
Adjust wash angles; coolant management; drying routines.
When surface treatments help
Thin dense/micro-cracked chrome mitigates rust initiation.
Corrosion, Lubricity, Dimensional Stability
| Concern | Controls (non-coating first) | When coatings help | Notes |
|---|---|---|---|
| Corrosion | Scrapers + covers; coolant chemistry; drying protocol | Chromium-family thin dense on rails/blocks | Re-map height/straightness post-coat |
| Lubricity | Oil metering; reduce seal drag; moderate preload | Low-Ra hard chrome reduces fretting/false brinelling | Coatings complement lube—don’t replace it |
| Dimensional stability | Fixed+floating; joint alignment; torque mapping | Controlled-thickness coatings; verify after install | Roller rails reveal base errors sooner than ball rails |
Frequently Asked Questions
Top speed is often lower for a given preload/seal set because contact and seal drag are higher. Oil supply and low-drag seals help.
More than ball rails. Line contact amplifies flatness/parallelism issues. Always torque-map during setup and adjust the slave rail.
Yes—micron-level height and straightness can shift. Re-map after coating and re-shim as needed.
Partner With Us
Upload it for a no‑fluff diagnostic checklist. We’ll map symptoms → checks → next actions (and only propose coatings when they’re truly indicated).
