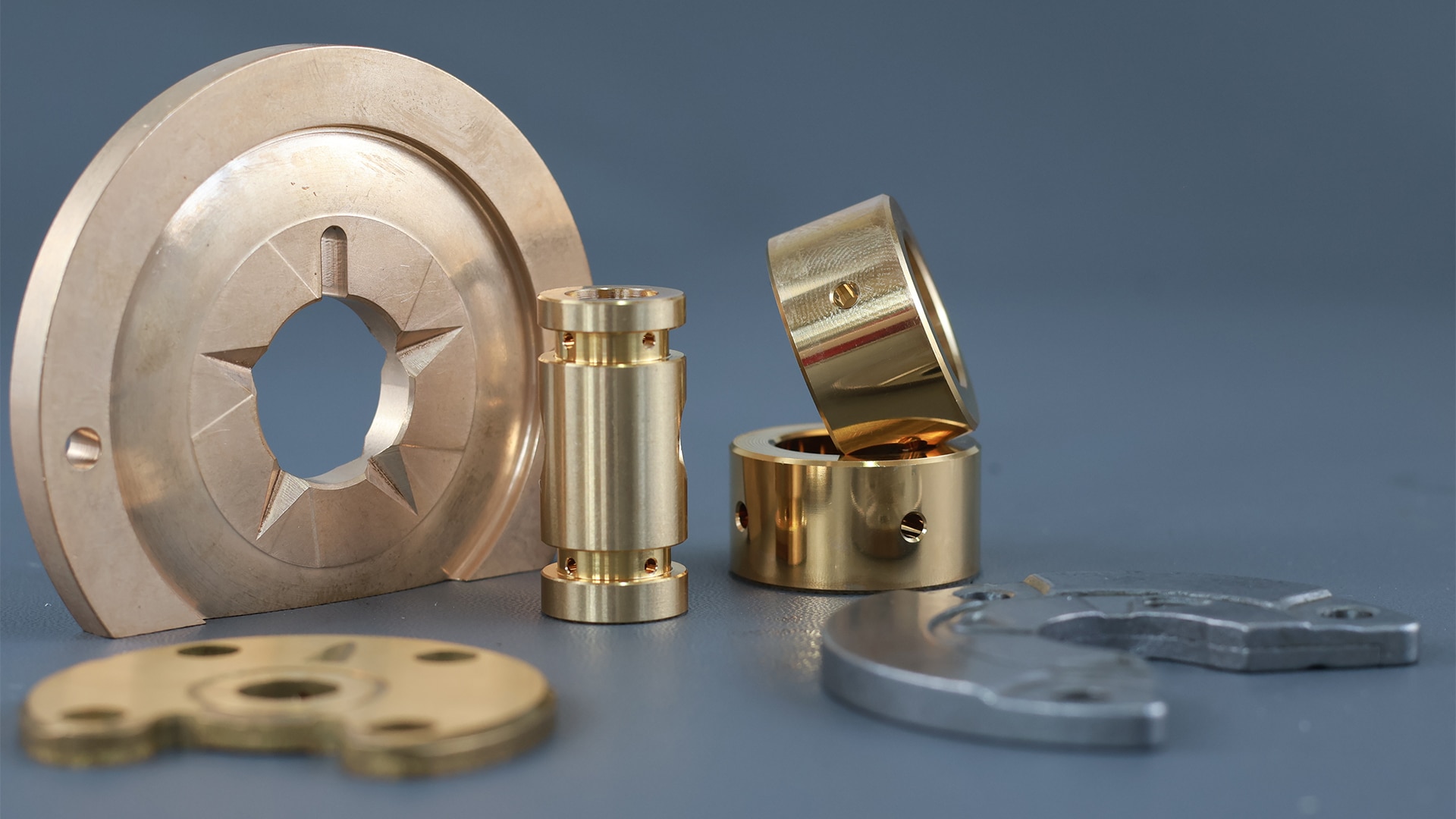
What Is a Journal Bearing?
A journal bearing supports a rotating shaft on a fluid film (oil, water, or gas) rather than rolling elements. In hydrodynamic designs, rotation generates the pressure; hydrostatic designs use an external pump; hybrids combine both. They offer very high radial load capacity, excellent damping, and quiet operation—but require the right clearance, alignment, and lubrication to avoid mixed/boundary contact at start/stop.
Typical uses: turbomachinery (compressors, turbines), motors/generators, gearboxes, heavy process equipment,
marine shafts, high-speed blowers, paper machines, and water-lubricated pumps.

Selection Cheatsheet (Duty → Geometry → Clearance → Oil)
- Duty & regime: continuous speed → hydrodynamic; frequent start/stop or very low speed → hydrostatic or hybrid.
- Load & L/D: high unit load → higher L/D or tilting-pad; high speed → manage temperature rise and stability.
- Clearance ratio: set from viscosity, speed, and diameter; verify minimum film thickness across worst-case misalignment.
- Grooves & supply: choose inlet groove scheme and flow path; for hydrostatic, size restrictors/pads for stiffness.
- Alignment: shaft/housing TIR and squareness drive film wedge; misalignment can collapse film at edges.
- Filtration: oil cleanliness is life—spec a β-rated filter and monitor ΔP; ensure breather/venting.
- Standby/corrosion: if exposed to water/chemicals, protect journals & seats (materials/coatings) and plan dry-out.
Journal Bearing Types — Quick Comparison
Pick a geometry that matches speed, load, and stability needs. Design clearance, grooves, and oil supply around your duty cycle.
Fixed (Cylindrical) Sleeve
SimpleCost-effective
- Hydrodynamic wedge forms via eccentricity; requires minimum speed to lift.
- Strengths: simplicity, broad availability, low cost.
- Watch-outs: subsynchronous whirl at high speed; edge loading with misalignment.
- Uses: general pumps, motors, gearboxes with steady speeds.
Two-Lobe (Lemon / Elliptical)
StabilityHigh speed
- Ellipticity preloads the film to reduce cross-coupled stiffness and whirl.
- Strengths: better stability margin vs. plain cylindrical at high speeds.
- Watch-outs: tighter machining tolerance; clearance distribution is critical.
- Uses: compressors, turbines, high-speed blowers.
Pressure-Dam / Offset-Groove
Lift assistStability
- Inlet/dam features raise local pressure to increase load & damping.
- Strengths: improved start-up behavior and rotordynamic stability.
- Watch-outs: geometry too abrupt can promote cavitation; validate groove CFD/hand-calc.
- Uses: high-speed shafts needing margin without moving pads.
Tilting-Pad (TPJB)
Wide speed rangeTop stability
- Pads pivot to self-form wedges; excellent damping & stability.
- Strengths: tolerant of misalignment; robust against whirl.
- Watch-outs: cost/complexity; monitor pad temperatures and pivot wear.
- Uses: turbomachinery, critical high-speed rotors.
Hydrostatic
Zero-speed liftHigh stiffness
- External pump supplies pressure; carries load at standstill.
- Strengths: start/stop friendly; superb positional stiffness.
- Watch-outs: restrictor design, contamination sensitivity, power draw.
- Uses: machine tools, heavy mills, precision positioning.
Hybrid (Hydrostatic + Hydrodynamic)
Wide dutyLow losses
- Hydrostatic lift for start/stop; transitions to hydrodynamic at speed.
- Strengths: reduced wear & power at cruise with safe low-speed behavior.
- Watch-outs: switchover control, restrictor/flow management, system complexity.
- Uses: variable-speed process equipment with frequent cycling.
Environment → Attributes Matrix
| Environment/Duty | Material / Lining | Clearance | Sealing | Lubricant / Supply | Notes |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| General oil-bath / circulating | Babbitt or bronze shell; steel journal | Per OEM; verify thermal growth | Non-contact labyrinth + breather | Mineral or synthetic; β-rated filtration | Monitor temperature rise and varnish |
| Frequent start/stop / low speed | Tilting-pad or hydrostatic; robust lining | May increase for mixed regime margins | Face seals or improved labyrinths | Hydrostatic supply or high-VI oil | Consider anti-seizure journal coatings |
| Contaminated / abrasive | Harder linings or polymer composites | Maintain nominal; avoid debris trapping | Tight labyrinth + exclusion devices | Upgraded filtration; offline kidney loop | Set ISO cleanliness targets; monitor ferrous wear |
| Water-lubricated | Polymer/graphite/carbon; corrosion-resistant hardware | Per supplier; hydrodynamic profile differs | Seal out grit; flush paths | Clean water supply; flow-assurance | Journal protection against standby corrosion |
| High temperature | High-temp babbitt/bronze or polymer spec | Account for viscosity drop & expansion | Heat shields; venting | Synthetic high-VI; cooling circuit | Check creep/softening limits of lining |
Common Failures & Diagnostics
Rapid Triage
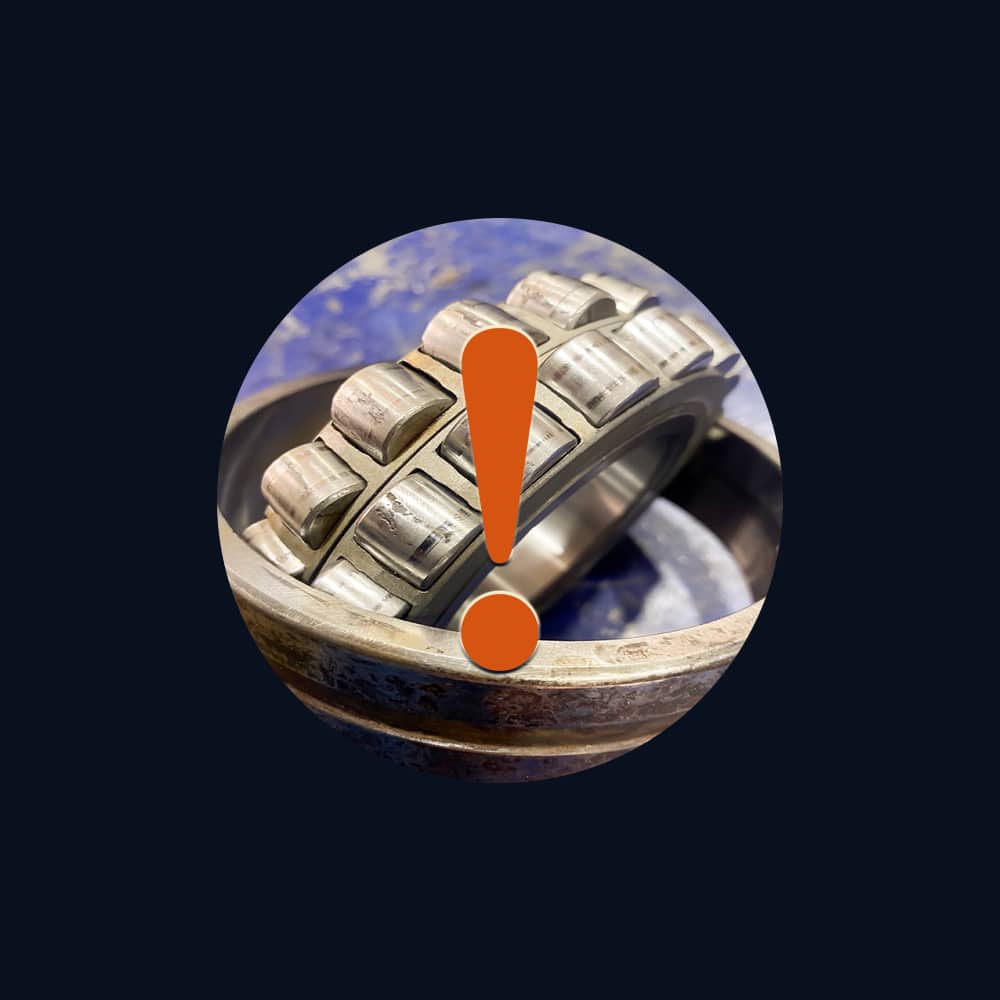

1) Wiping / Seizure (Boundary Contact)
Symptoms
Sudden temperature spike, metallic smell, smeared lining, shaft scoring.
Likely causes
Insufficient oil, too tight clearance, start/stop without lift, misalignment.
Checks
Flow/pressure, viscosity at operating temp, film calc, alignment/TIR.
Non-coating actions
Restore supply, adjust clearance, add hydrostatic lift or warm-up sequence, correct alignment.
When surface treatments help
Low-roughness hard chrome on journal can improve scuff resistance during brief upsets.
2) Lining Fatigue / Spalling
Symptoms
Subsurface cracks, flakes in sump, rising vibration.
Likely causes
High unit load, thermal softening, dynamic instability, misalignment edge loading.
Checks
Unit pressure (P), temperature margin, modal stability, contact pattern.
Non-coating actions
Increase bearing area/L/D, switch to tilting-pad, improve cooling, correct alignment.
When surface treatments help
Not primary—geometry, material, and cooling dominate.
3) Cavitation Erosion
Symptoms
Honeycomb pitting near trailing edge/inlet, noise.
Likely causes
Low inlet pressure, abrupt groove geometry, high ΔP.
Checks
Supply pressure, groove pattern CFD/hand-calc, inlet restrictions.
Non-coating actions
Increase inlet pressure/flow, smooth transitions, redesign grooves.
When surface treatments help
Hard, inert chrome on journals resists erosion if contact occurs; still fix hydraulics first.
4) Corrosion / Water Ingress
Symptoms
Rust staining on journals at seals, emulsified oil, bearing discoloration.
Likely causes
Faulty seals/breathers, washdown, condensation, incompatible oil additive pack.
Checks
Water ppm, seal condition, breather spec, cleaner pH.
Non-coating actions
Improve sealing & venting, upgrade oil & dehydration, add standby turning/dry-out.
When surface treatments help
Chrome/Ni-P on journals & seats slows corrosion between runs.
The Big Three: Corrosion, Lubricity (Mixed Regime), Dimensional Stability
Surface treatments target journals, sleeves, and seats—not the soft bearing lining. Use coatings to resist scuff/corrosion during mixed or boundary conditions, but do not substitute coatings for proper clearance, oil, or alignment.
| Concern | What it means | Non-coating controls (first) | When coatings help | Notes |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Corrosion resistance | Protect journals/bores from water/chemical attack, especially during standby | Seals, breathers, dry-out routines, compatible oil | Thin dense/micro-cracked chrome or Ni-P on journals & seats | Validate post-process roundness and surface finish |
| Lubricity (mixed) | Reduce scuff during start/stop or upset when film collapses | Hydrostatic lift, higher VI oil, correct warm-up, groove tuning | Low-roughness hard chrome on journals improves scuff resistance | Coatings complement, not replace, oil film formation |
| Dimensional stability | Hold clearance after any processing; avoid geometry drift | Measure roundness/TIR; thermal model; set clearance per duty | Controlled-thickness coatings with post-grind/polish | Micron-level thickness changes shift clearance significantly |
Quick Calculators (Engineering Aids)
- Sommerfeld number (order-of-magnitude): S ∝ (μ·N/p)·(R/c)2 → stability & film thickness trend.
- Minimum film: use OEM/handbook/tilting-pad correlations; check worst-case misalignment.
- Power loss & ΔT: estimate shear loss → size cooler; ensure oil inlet temperature margin.
Have a failure photo, sound clip, or spec?
Upload it for a no‑fluff diagnostic checklist. We’ll map symptoms → checks → next actions (and only propose coatings when they’re truly indicated).
