Surface Finishing with Zinc
The Best Ally of Steel to Combat Corrosion
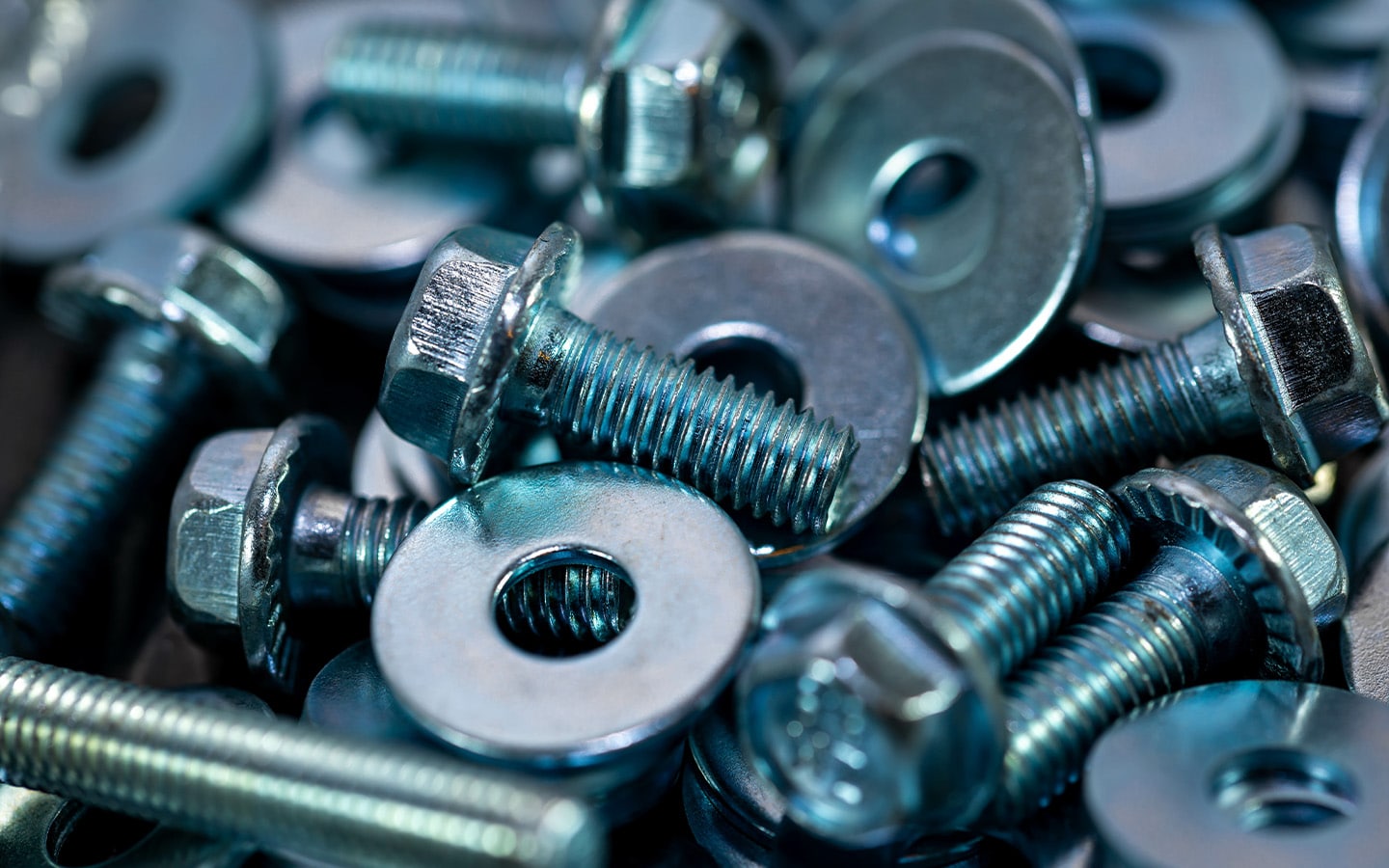

An Economical Way to Prevent Corrosion
The Armoloy Corporation helps manufacturers safeguard their high-precision metal components with a diverse portfolio of coating technologies.
The popularity of zinc plating stems from its cost-effectiveness and the comprehensive protection it offers against corrosion. It’s an economical alternative to more expensive finishes and is applicable to small components as well as large structures. Various post-treatment options are available, such as passivation and chromate conversion, which can impart additional properties like increased resistance to white rust or enhance the aesthetic appeal of the zinc-finished surface.
Zinc Plating Highlights
- Corrosion and oxidation resistance
- Reduces abrasion and wear
- Creates a non-toxic surface
- Chromate conversion for increased corrosion protection
- Cost-effective and ease of application
- Undercoat for paint applications
- Low stress deposit
- Improves lubricity
Proven applications
Zinc can improve the long-term performance of all the following industry-specific applications and more.
- Automotive components
- Nuts
- Bolts
- Washers
- Stainless steel structures
- Construction equipment
- Electronic components
- ASTM B633-11 (Type I & III)
- AMS 2402
- REACH compliant
- AMS 2417
- ELV compliant
- WEEE compliant

Zinc Plating Features & Benefits
Corrosion resistance
Zinc plating provides a protective barrier that shields the base metal from corrosive elements, significantly extending the life of the part by preventing rust
Cost-effective
Comparing to other metal finishes such as silver plating, zinc plating is more economical, making it a cost-effective solution for corrosion protection of high-volume parts
Aesthetic flexibility
Parts can be passivated or chromated to produce various colors and finishes, enhancing the visual appeal of the products and allowing customization to meet specific aesthetic requirements
Increased durability
The zinc coating enhances the overall strength and durability of the metal part, helping it withstand physical and environmental stressors better than uncoated metals
Temperature tolerance
Zinc maintains its integrity under a range of temperatures, which makes it suitable for use in varying climatic conditions without degradation of the protective qualities
Eco-friendly
Zinc is a non-toxic and recyclable material, making zinc plating a more environmentally friendly option compared to other coatings like cadmium
Sacrificial coating
Zinc acts as a sacrificial layer, corroding before the underlying metal does, which offers further protection against corrosion, especially in harsh environments
The Science Behind Zinc

How it Works
Zinc plating involves several key steps, beginning with thorough cleaning of the substrate to remove any contaminants. This is usually done using an alkaline detergent followed by a rinse, and sometimes an acid pickling to prepare the surface. The clean parts are then immersed in a plating bath containing a zinc solution, where they act as the cathode. Applying an electric current facilitates the transfer of zinc ions from the solution onto the substrate. The amount of zinc that gets deposited can be controlled through the current density, bath temperature, and zinc concentration in the bath.
The zinc forms as a sacrificial anode, corroding itself in preference to the underlying metal. After plating, various finishing touches can be applied, such as chromating to enhance corrosion resistance or dying to improve appearance. The final properties of the zinc coating, including its thickness and appearance, can be tailored according to the specific requirements of the application, making zinc plating a versatile and widely used metal finishing process.
Services at Armoloy
The Armoloy Corporation is here to provide support for your project, starting from the discovery phase and continuing through a successful production launch. Whether coatings are considered during the initial part design phase or become necessary due to product failures in the field, our team can assist you at any stage in the process.




Partner With Us
Improve metal surface performance to its highest pinnacle. Meet our group of curious, innovative engineers and learn how we can help improve your industry with science-based solutions like our nickel chrome plating.