Plating and Testing Standards at Armoloy
Armoloy certifies to a wide range of plating and testing specifications, including standards developed by SAE International (AMS series) and ASTM International. These standards specify key properties like plating thickness, adhesion, corrosion resistance, and surface hardness to meet industrial and engineering requirements.
Below are common specifications supported at Armoloy locations worldwide.
Services at Armoloy
The Armoloy Corporation is here to provide support for your project, starting from the discovery phase and continuing through a successful production launch. Whether coatings are considered during the initial part design phase or become necessary due to product failures in the field, our team can assist you at any stage in the process.

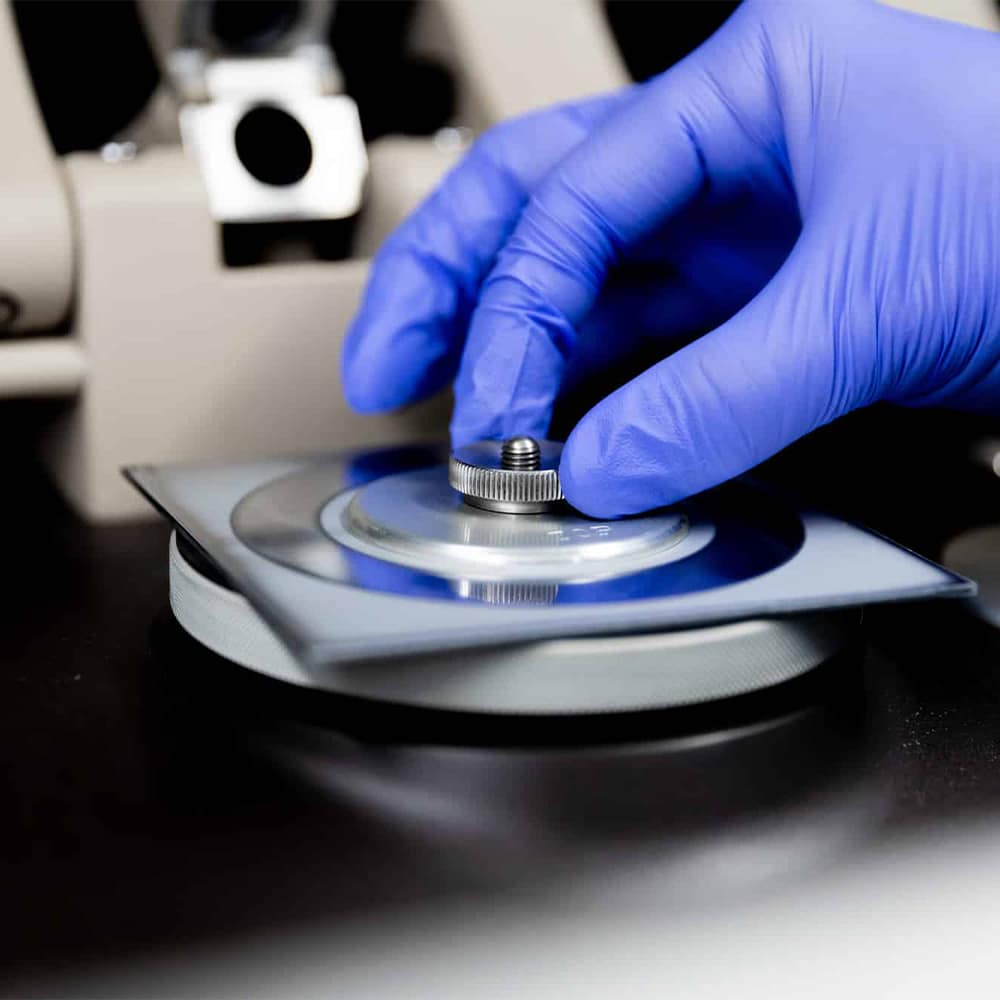

Partner With Us
Armoloy certifies to a wide range of industry plating and testing standards. Explore our specifications and accreditations or connect with us to meet your project needs.
Disclaimer: The interpretations and overviews of specifications provided by The Armoloy Corporation are solely the views of Armoloy and may not represent the views of other entities. These interpretations are intended for informational purposes only and should not be considered as definitive or legally binding. The Armoloy Corporation is not responsible for the accuracy of these interpretations and expressly disclaims any liability for loss or damage arising from their use. This disclaimer is subject to change and does not create any express or implied warranty regarding the information provided.
