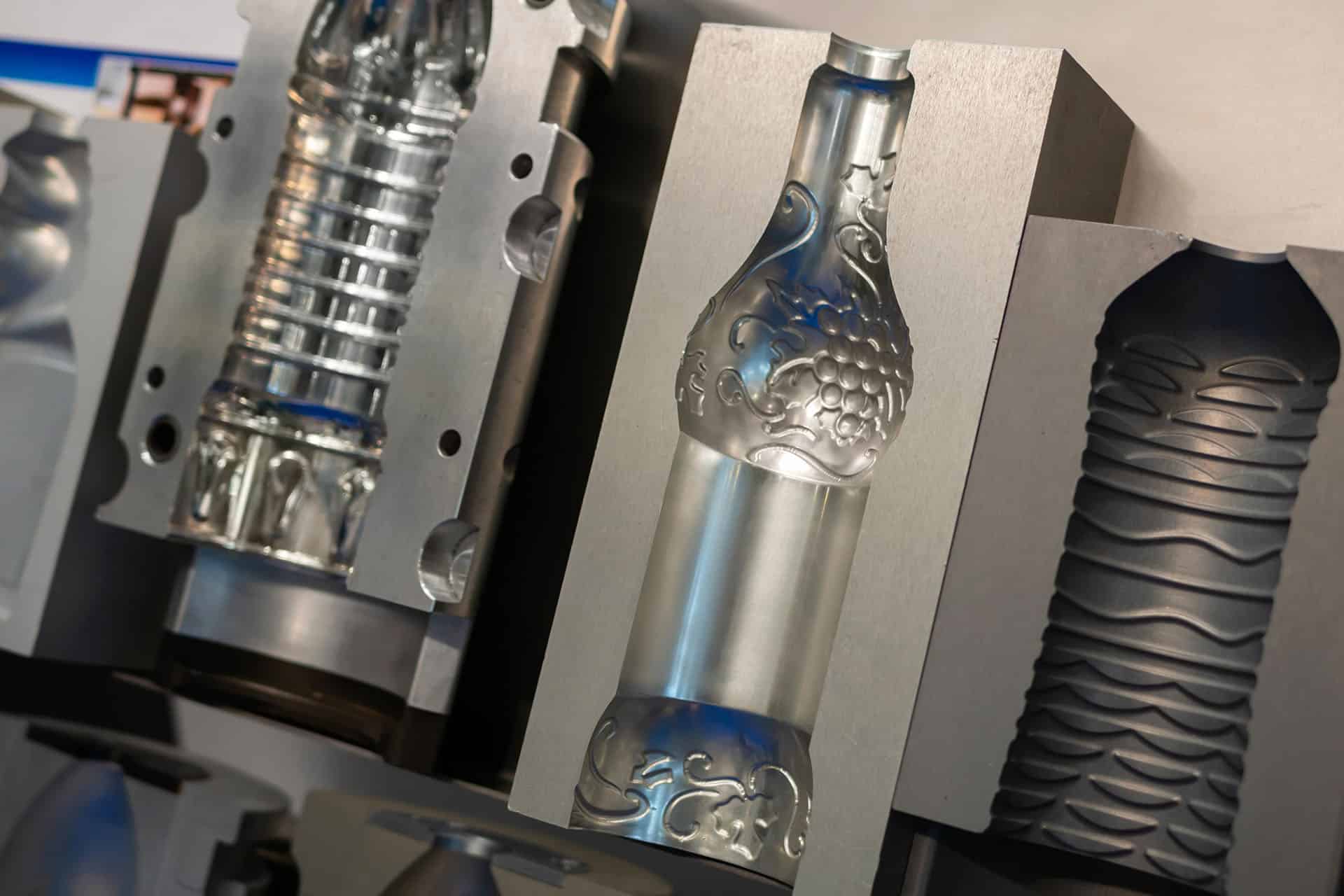
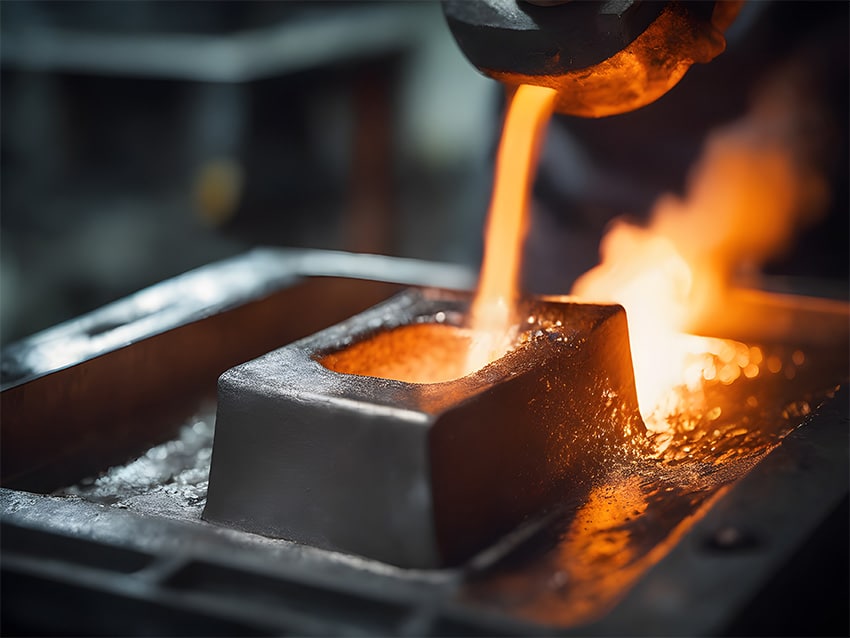
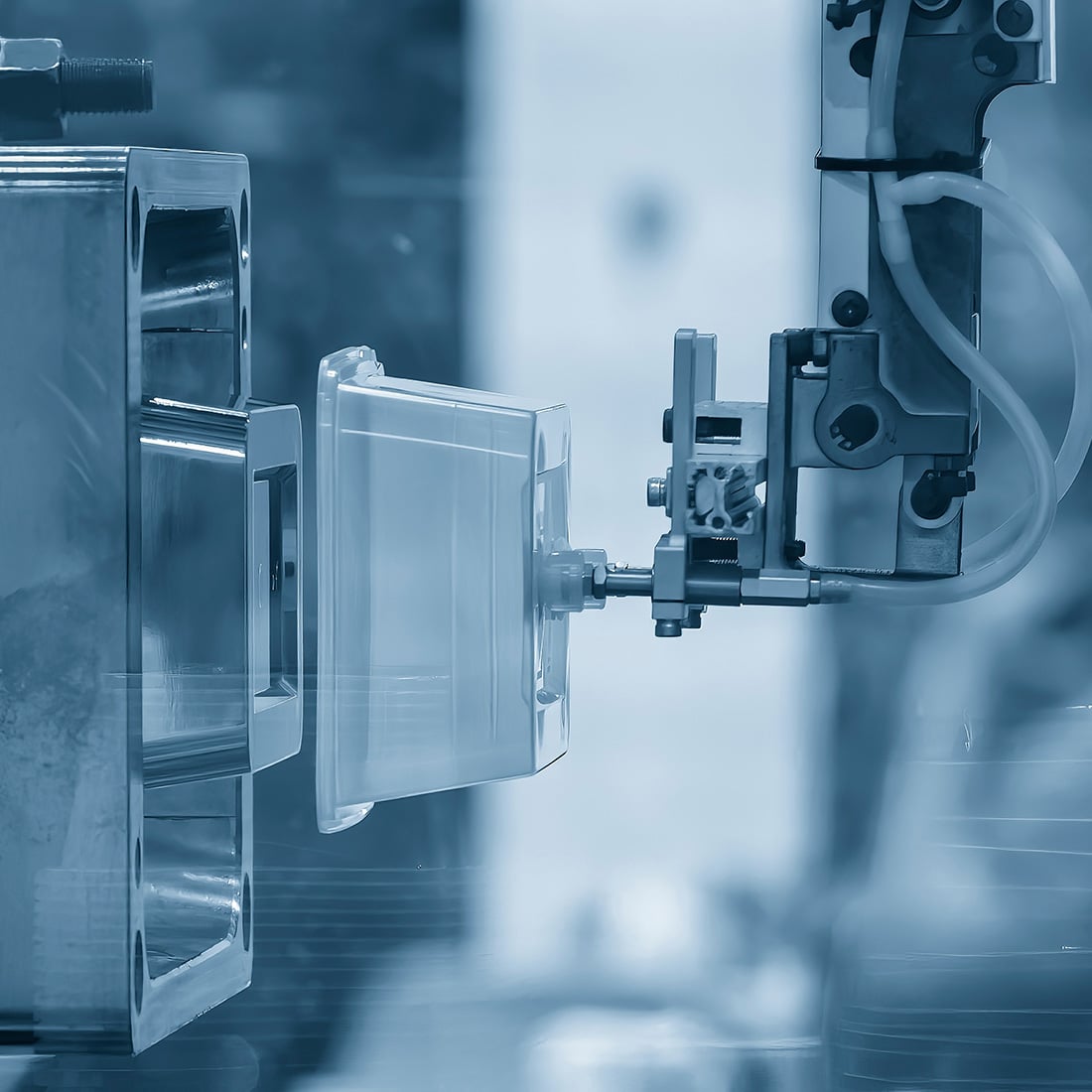
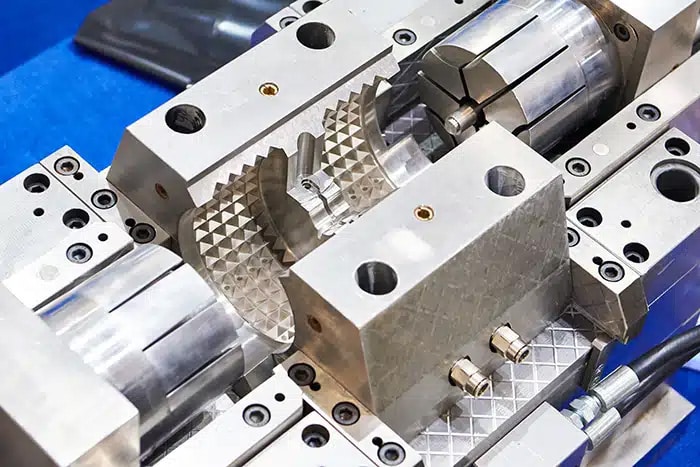
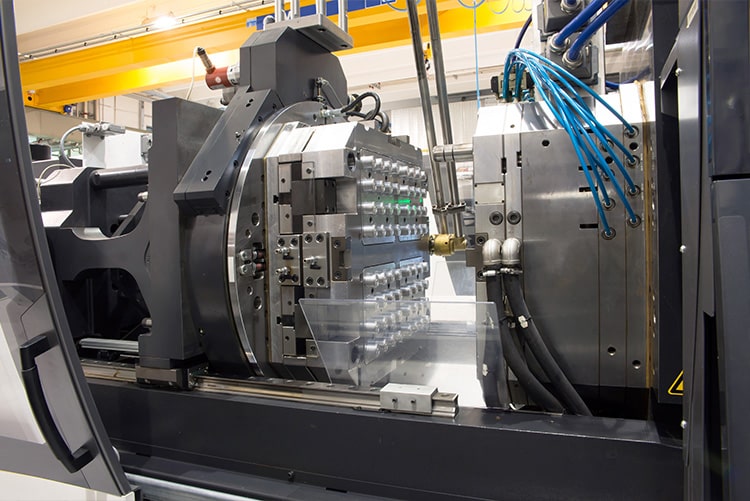
Mold release coatings play a critical role in injection molding and similar manufacturing processes by preventing plastic, rubber, or composite materials from adhering to mold surfaces. By reducing sticking, these coatings streamline part ejection, minimize buildup, and extend mold life — ultimately improving production efficiency and reducing downtime.
Different types of mold release coatings are available, each tailored to address specific performance needs:
- Metal Coatings (Electroplated or Electroless): Processes such as Thin Dense Chrome or electroless nickel plating deposit a uniform metallic layer that enhances corrosion resistance and withstands abrasive wear in high-cavity mold environments.
- CVD (Chemical Vapor Deposition): These coatings, including silicon carbide and boron nitride, are chemically bonded to the mold and deliver exceptional heat, abrasion, and chemical resistance for demanding molding applications.
- PVD (Physical Vapor Deposition): PVD films such as titanium nitride (TiN) and titanium carbonitride (TiCN) are used to boost surface hardness and resist wear under repetitive molding cycles.
- Oxide-Based Treatments: Surface treatments like anodizing or phosphating generate an oxide layer that improves both corrosion resistance and surface hardness, particularly for aluminum or steel molds.
- Thermal Spray Coatings: Using molten material such as ceramics, carbides, or metals, this method builds a thick, durable layer that protects molds from mechanical stress and thermal fatigue.
- Polymeric Coatings: Engineered polymers — such as polyurethane or polyether-based layers — provide low surface energy and strong chemical resistance, ideal for delicate mold surfaces requiring non-stick performance.
Whether the goal is to extend tool life, improve part release, or reduce cycle time, selecting the right mold coating is key to optimizing your injection molding operations.