The four primary types of wear are:
-
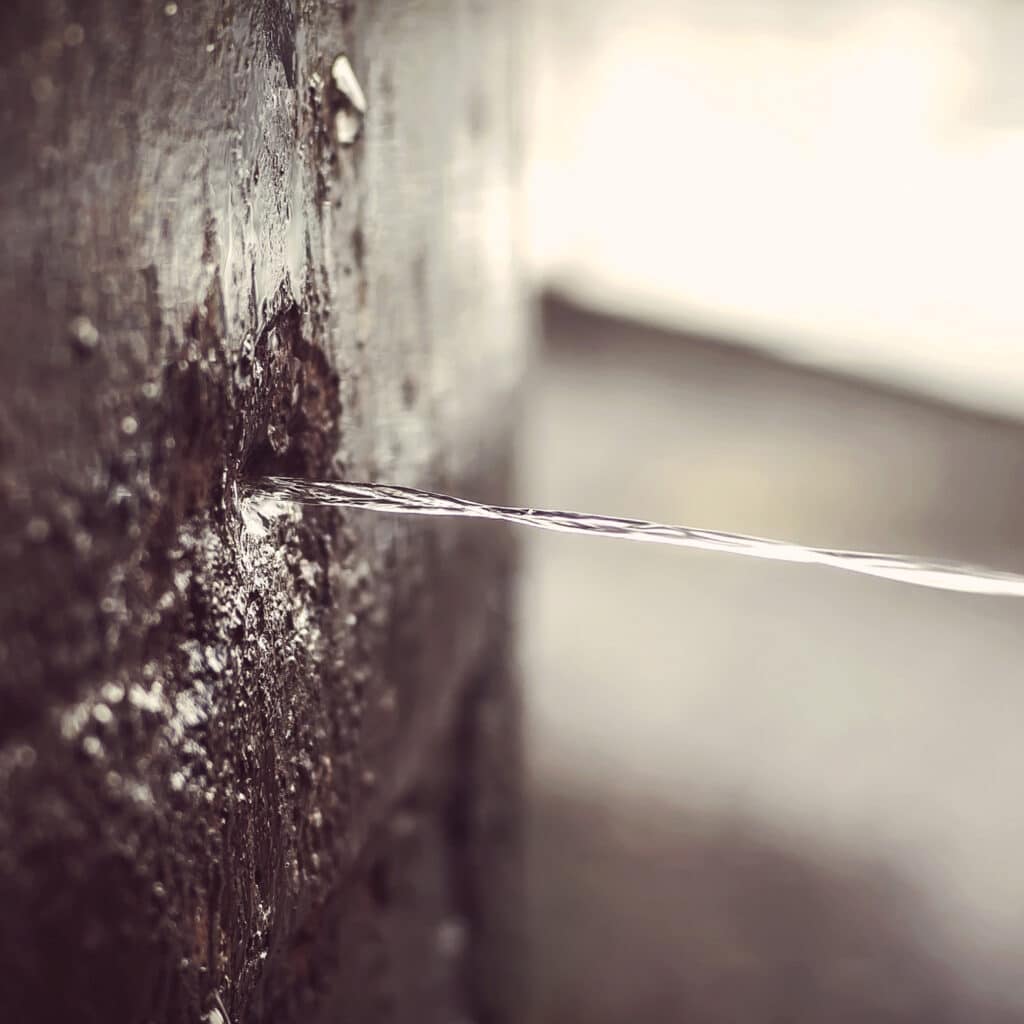
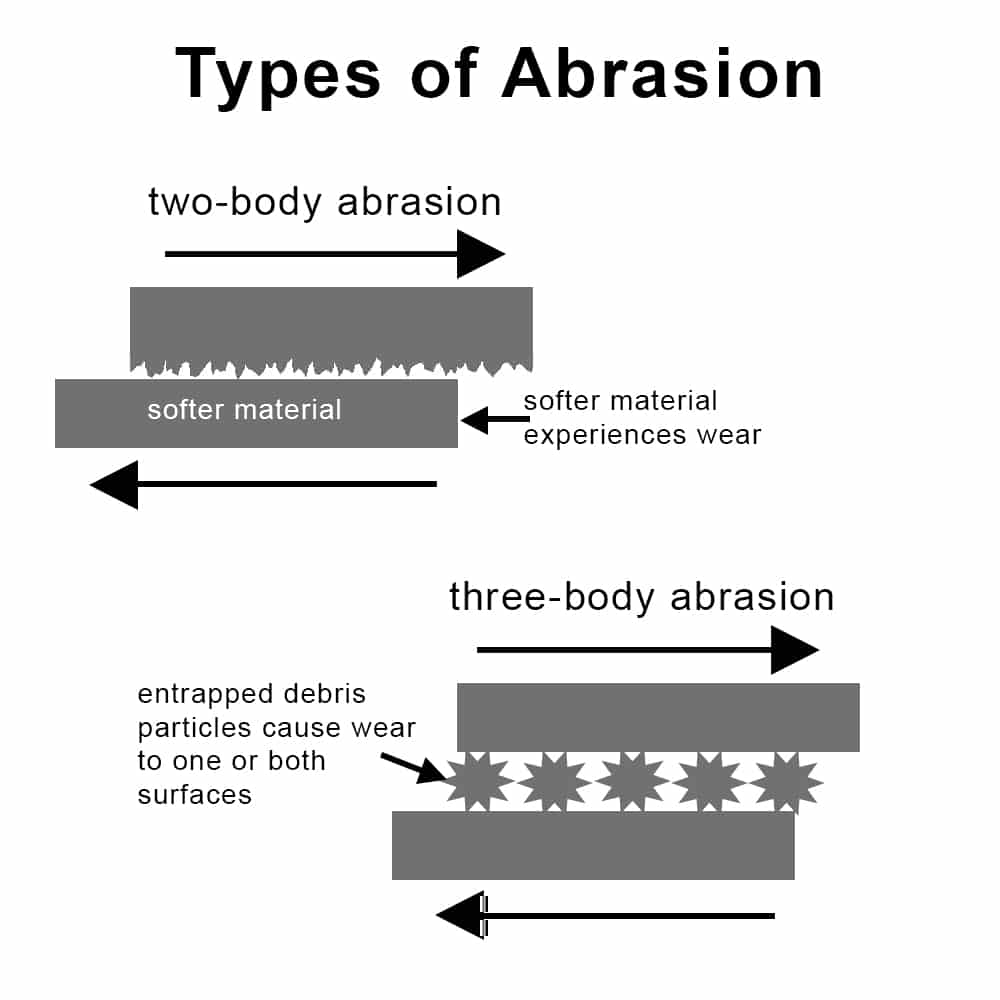
- Abrasive Wear: Occurs when hard particles or hard protuberances on a surface slide or roll across a softer surface, causing material removal. It is common in environments with high levels of dust or particulates.
- Adhesive Wear: Happens when two solid surfaces slide over each other, causing material transfer from one surface to another. This type of wear is often seen in metal-to-metal contact and can result in galling or seizing.
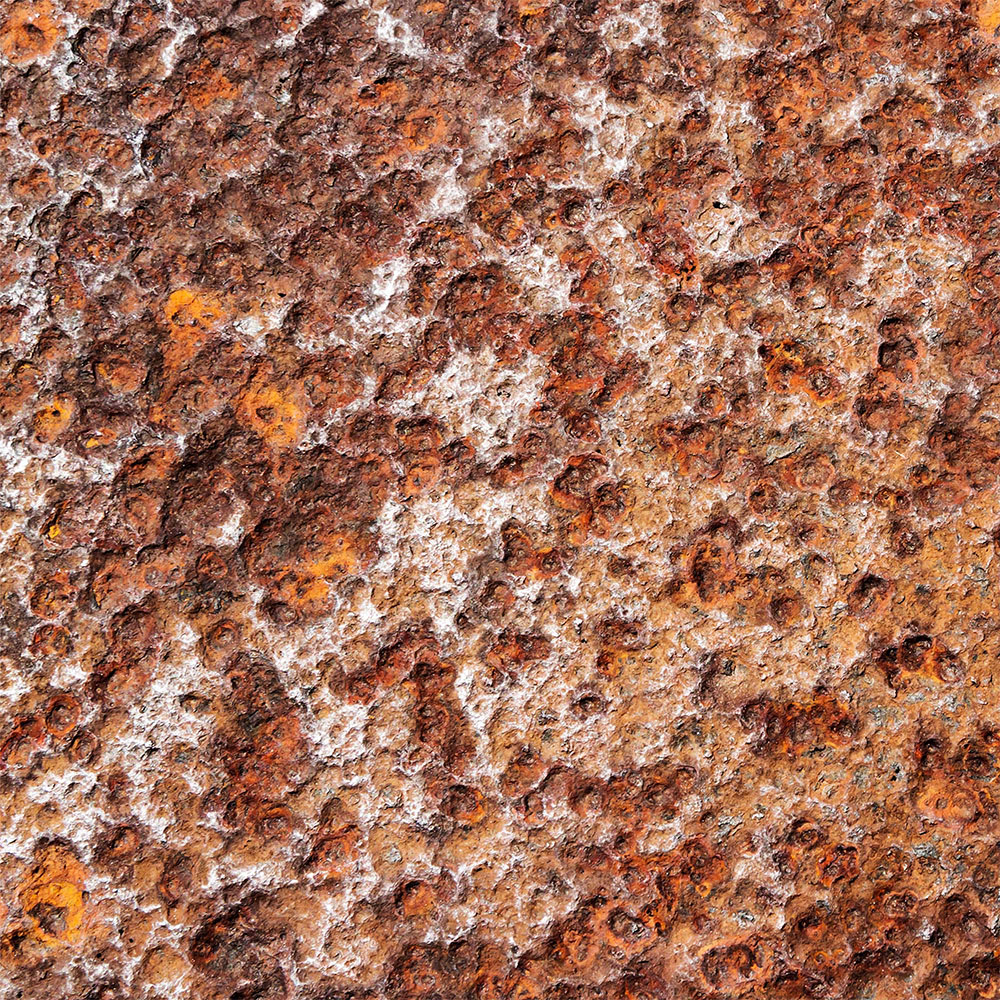
- Corrosive Wear: Combines chemical reactions with mechanical wear. Corrosive substances, such as acids or alkalis, degrade the material’s surface, which then wears away more easily when subjected to mechanical action.
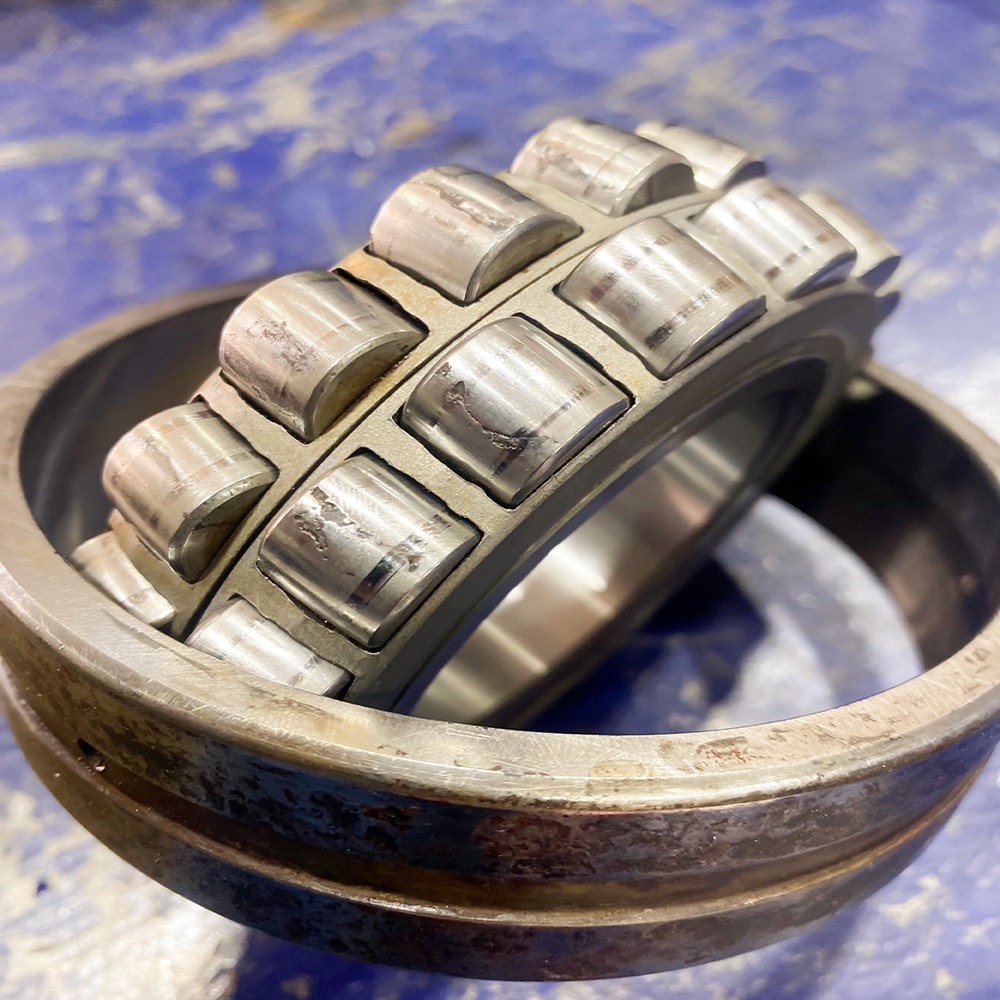
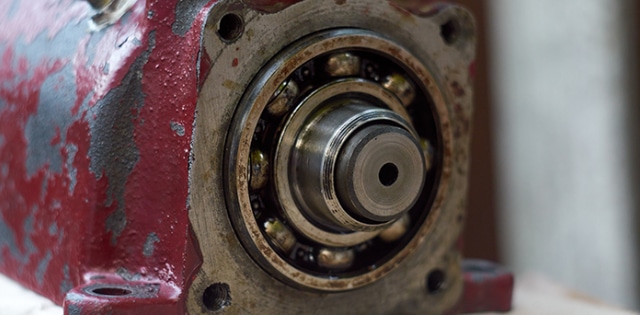
- Fatigue Wear: Caused by repeated loading and unloading cycles that lead to the formation of cracks and material flaking. This type of wear is prevalent in components subject to cyclic stresses, like bearings and gears.
Fatigue wear is often seen in bearings, gears, and rotating machinery where load cycles stress the material repeatedly over time.