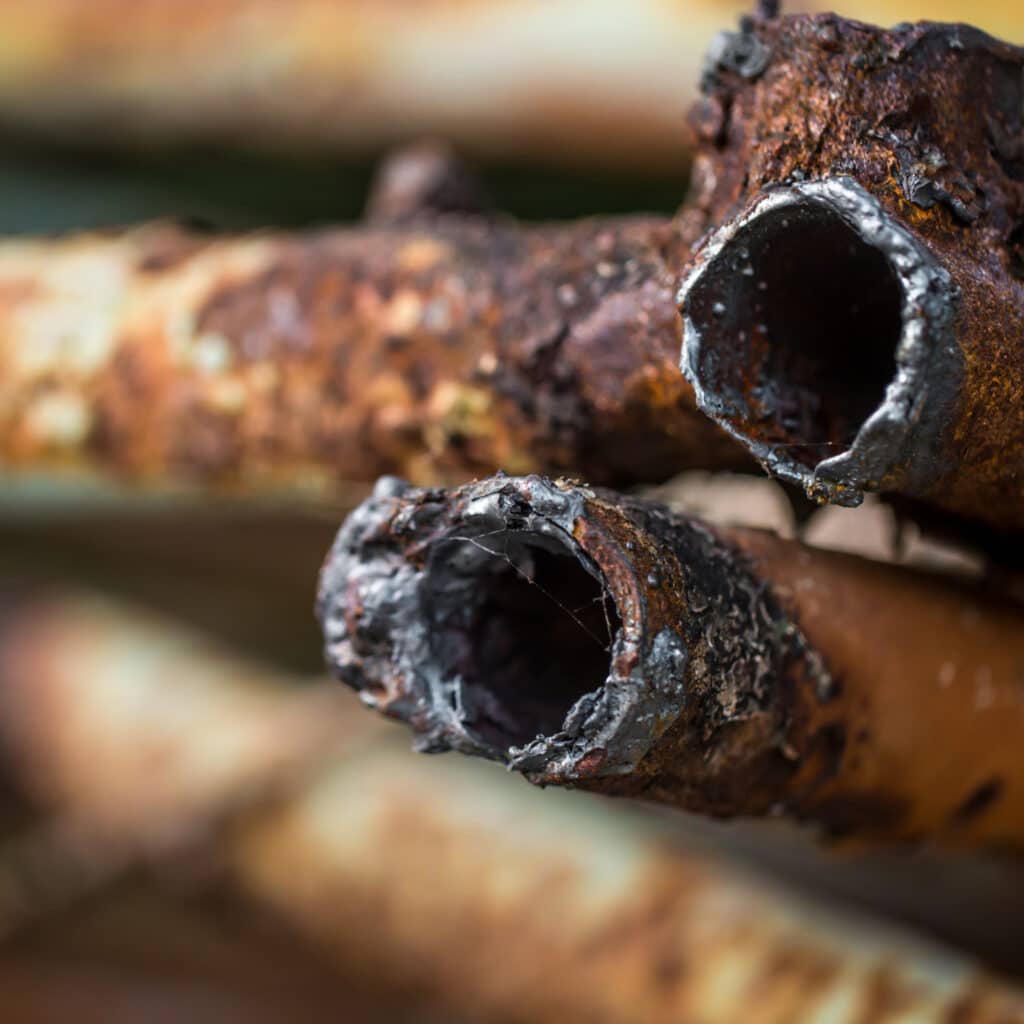
A classic example of erosive wear is seen in gas turbine engine blades. As air is drawn into the turbine at high speed, it often carries fine particles like dust, sand, or ash. These particles strike the blades repeatedly at high velocity, gradually wearing down the surface.
This repeated impact can cause surface pitting, edge rounding, and thinning of the blade profile — reducing both aerodynamic efficiency and structural strength over time.
How to prevent erosive wear in turbines:
- Air Filtration: Install high-efficiency air filters to capture particulates before they enter the intake system.
- Protective Coatings: Apply erosion-resistant surface coatings to extend blade life and resist particle impact damage.
- Routine Monitoring: Conduct scheduled inspections to detect early erosion and prevent more serious failures.
Managing erosive wear is critical in aviation, power generation, and other high-performance systems where surface integrity directly impacts safety and efficiency.