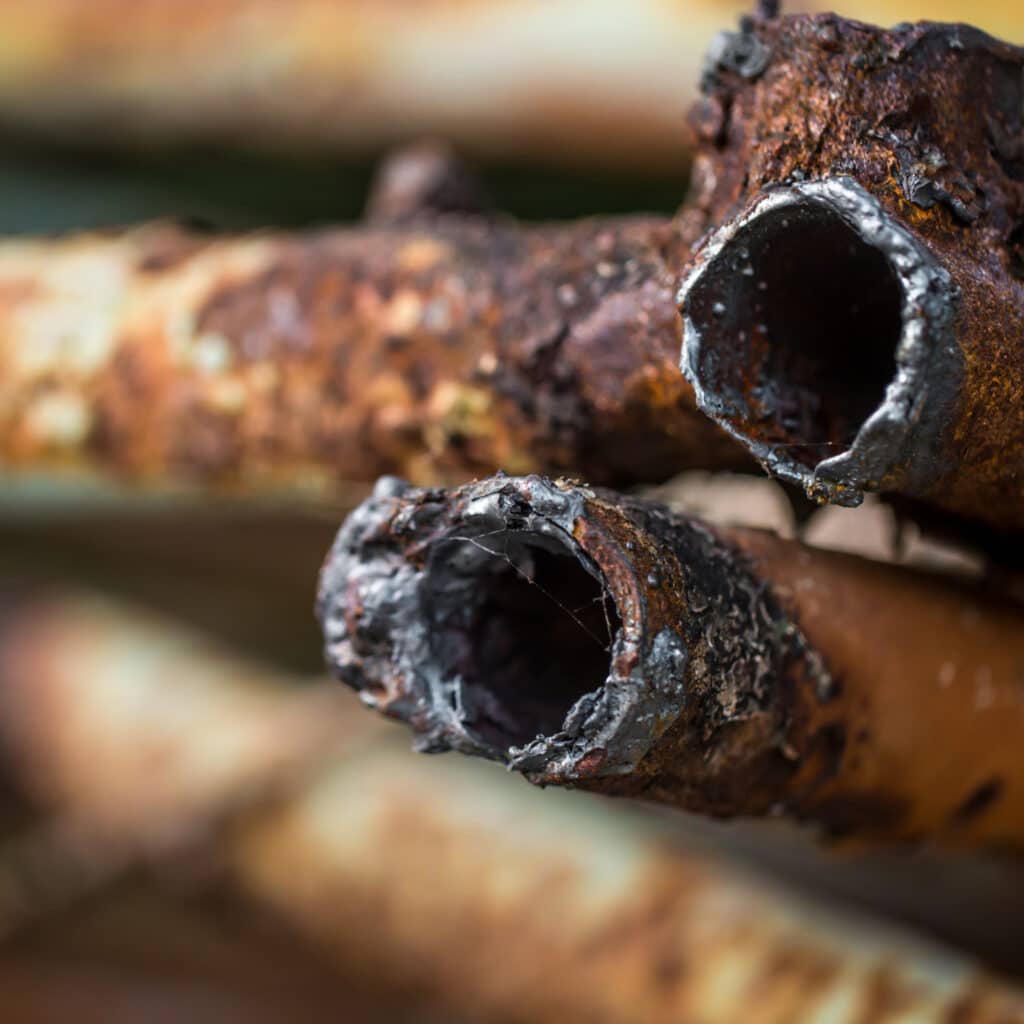
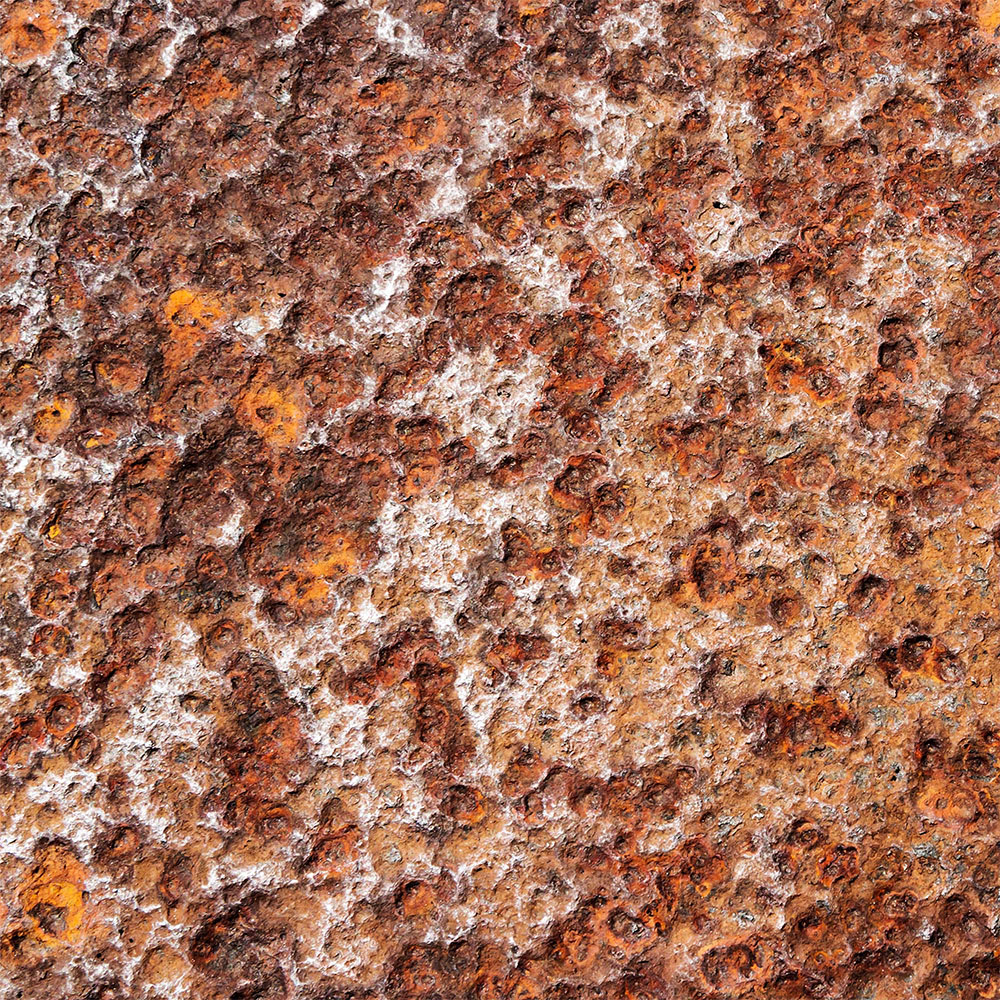
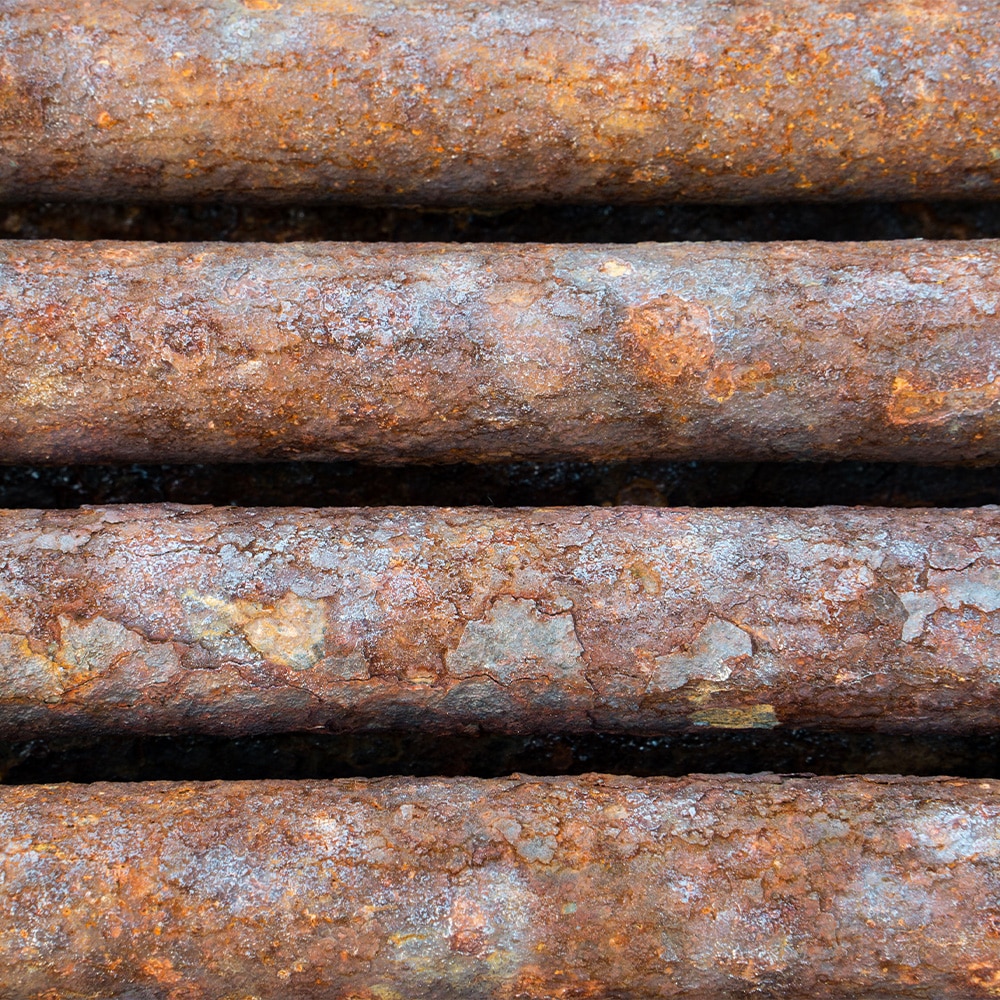
Corrosive wear is a type of material degradation that results from the combined effects of chemical attack and mechanical action. It typically develops in aggressive environments where protective surfaces break down over time. Here are the main contributing factors:
- Chemical Exposure: Contact with substances like acids, alkalis, salts, or oxidizers initiates chemical reactions that weaken the material surface.
- Mechanical Interaction: Erosion, abrasion, or repeated friction removes the compromised outer layer, revealing fresh material to ongoing chemical attack.
- Environmental Stressors: Extreme temperatures, high humidity, and salt-laden air (as found in marine settings) can significantly accelerate corrosive wear.
- Material Limitations: Metals or polymers lacking corrosion resistance or mechanical toughness are more likely to degrade quickly under stress.
- Contamination: Dirt, debris, or embedded particles promote both corrosion and mechanical wear by disrupting surface integrity.
- Electrochemical Reactions: When dissimilar metals are joined in the presence of an electrolyte, galvanic corrosion may occur — further accelerating wear at contact points.
To prevent corrosive wear, it’s important to use corrosion-resistant materials, apply protective coatings, and manage environmental and mechanical conditions through design and maintenance strategies.