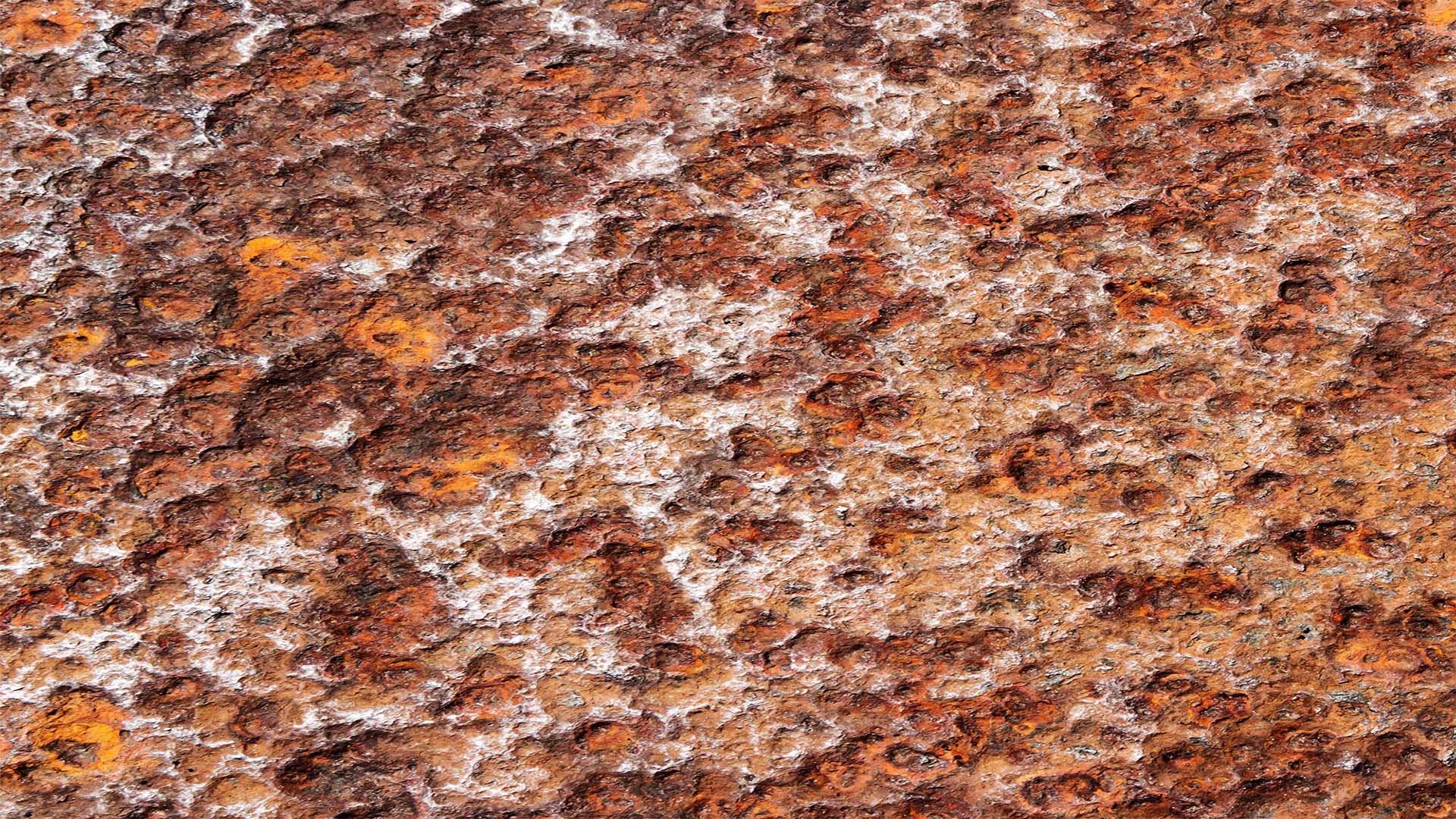
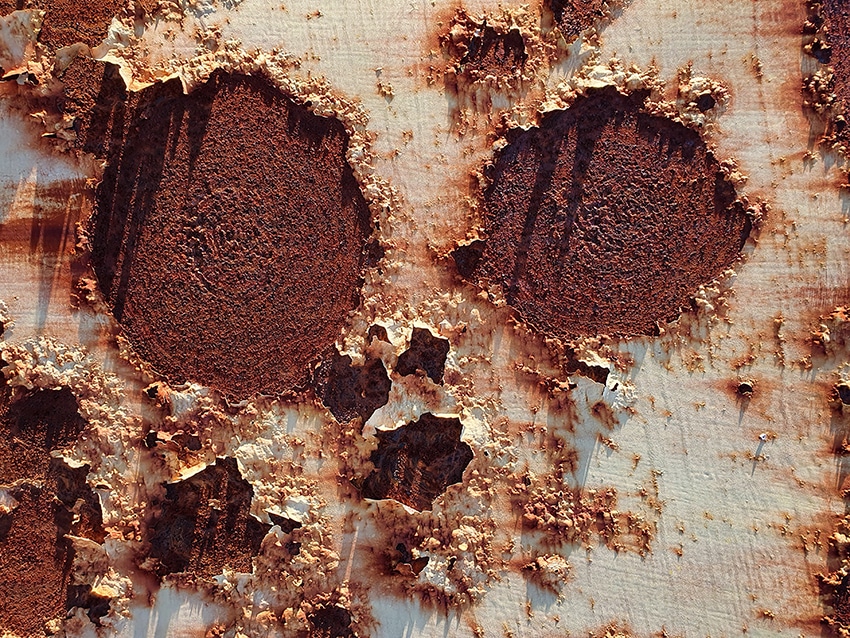
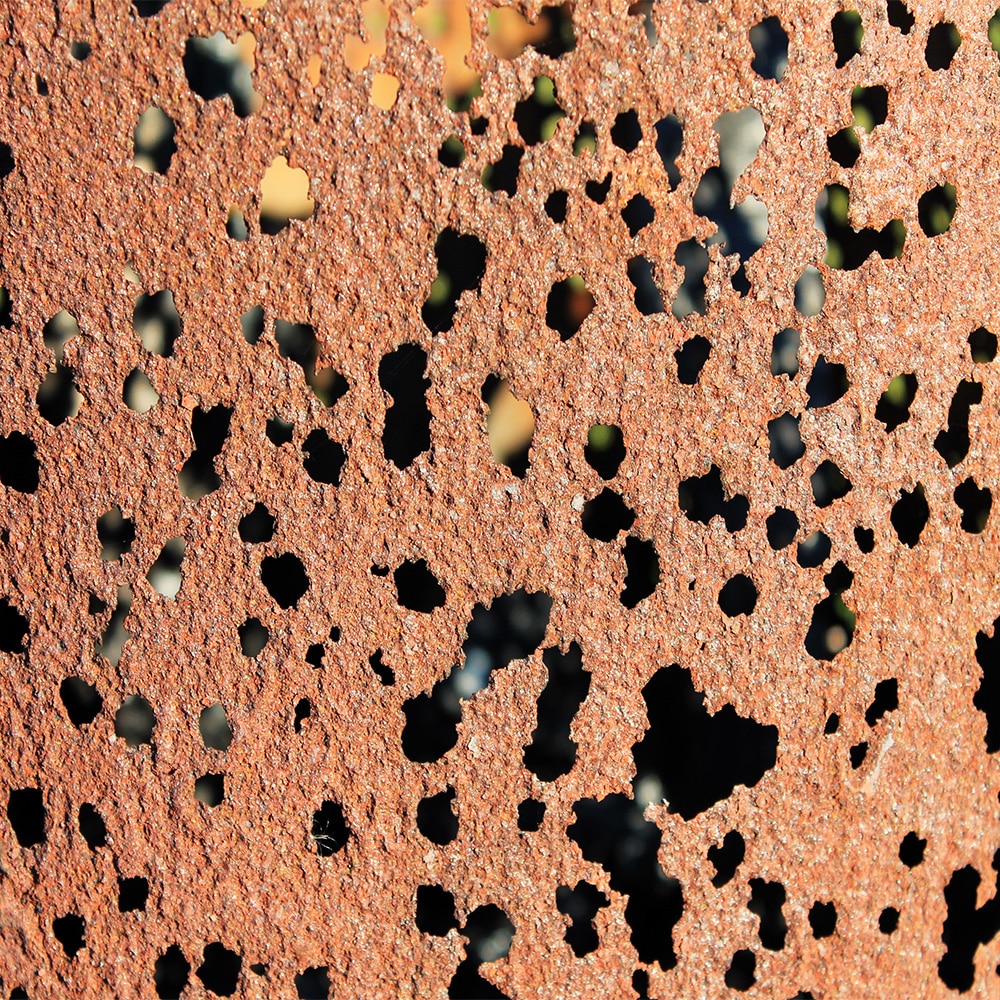
Pitting corrosion is a localized attack that forms small, deep holes in metal surfaces — often triggered by chlorides, stagnant fluids, or surface flaws. Addressing pitting requires both corrective action and long-term prevention.
How to Repair Pitted Surfaces:
- Surface removal: Grind, blast, or polish the affected area to eliminate corrosion pits and restore uniformity.
- Structural repair: Fill deeper pits using weld overlays or metal-filled epoxies if the damage threatens strength or pressure containment.
- Restore protection: Reapply corrosion-resistant coatings like thin dense chrome, nickel, epoxies, or industrial paints.
How to Prevent Pitting in the Future:
- Select better alloys: Use high-performance stainless steels (e.g., 316, duplex) with strong pitting resistance numbers (PREN).
- Design for drainage: Avoid crevices and stagnant zones where moisture or chemicals can collect.
- Apply protective barriers: Use coatings or chemical inhibitors in corrosive service conditions such as marine or washdown areas.
- Maintain proactively: Rinse away salt or chemical buildup and inspect regularly to catch early signs of damage.
Preventing pitting is critical in components like tanks, heat exchangers, pumps, and stainless steel piping — where hidden localized corrosion can cause sudden failure even when the rest of the surface looks intact. Learn more at our full guide to pitting corrosion.