While both fatigue and creep are failure mechanisms in metals, they occur under very different service conditions and stress behaviors.
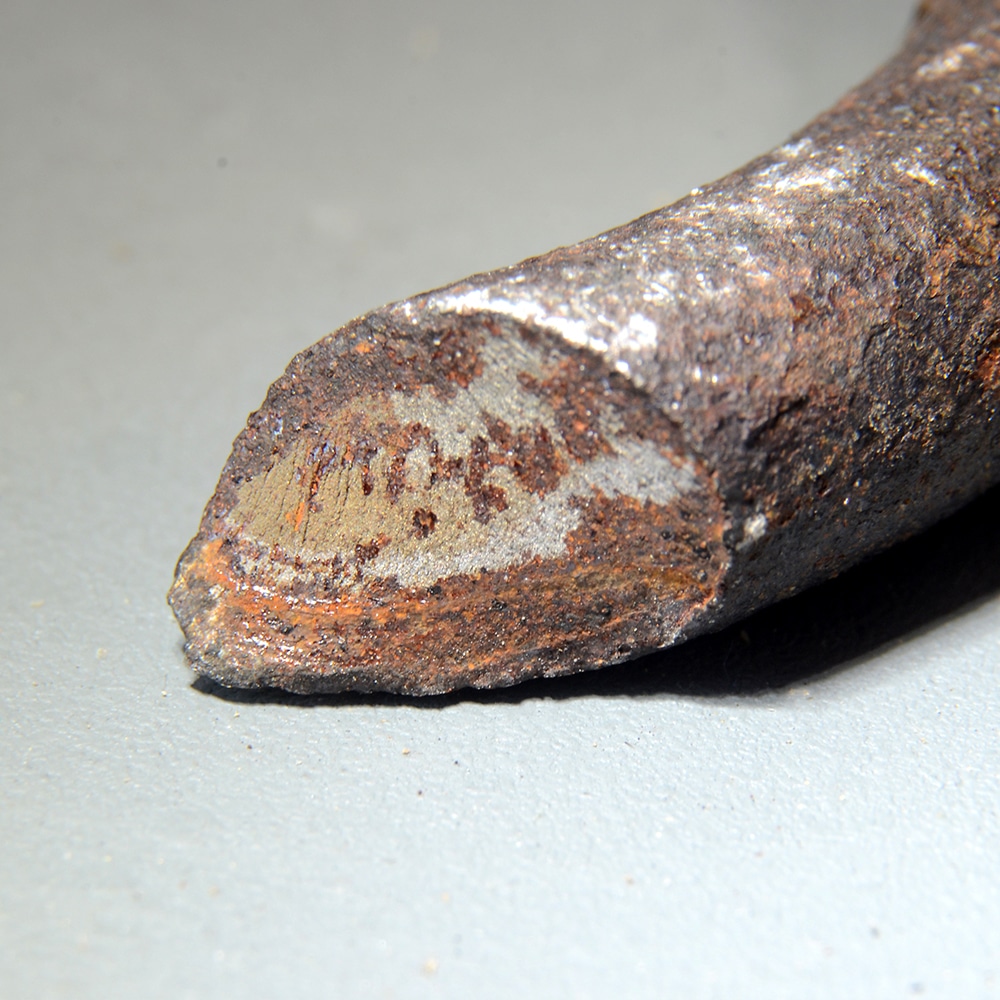
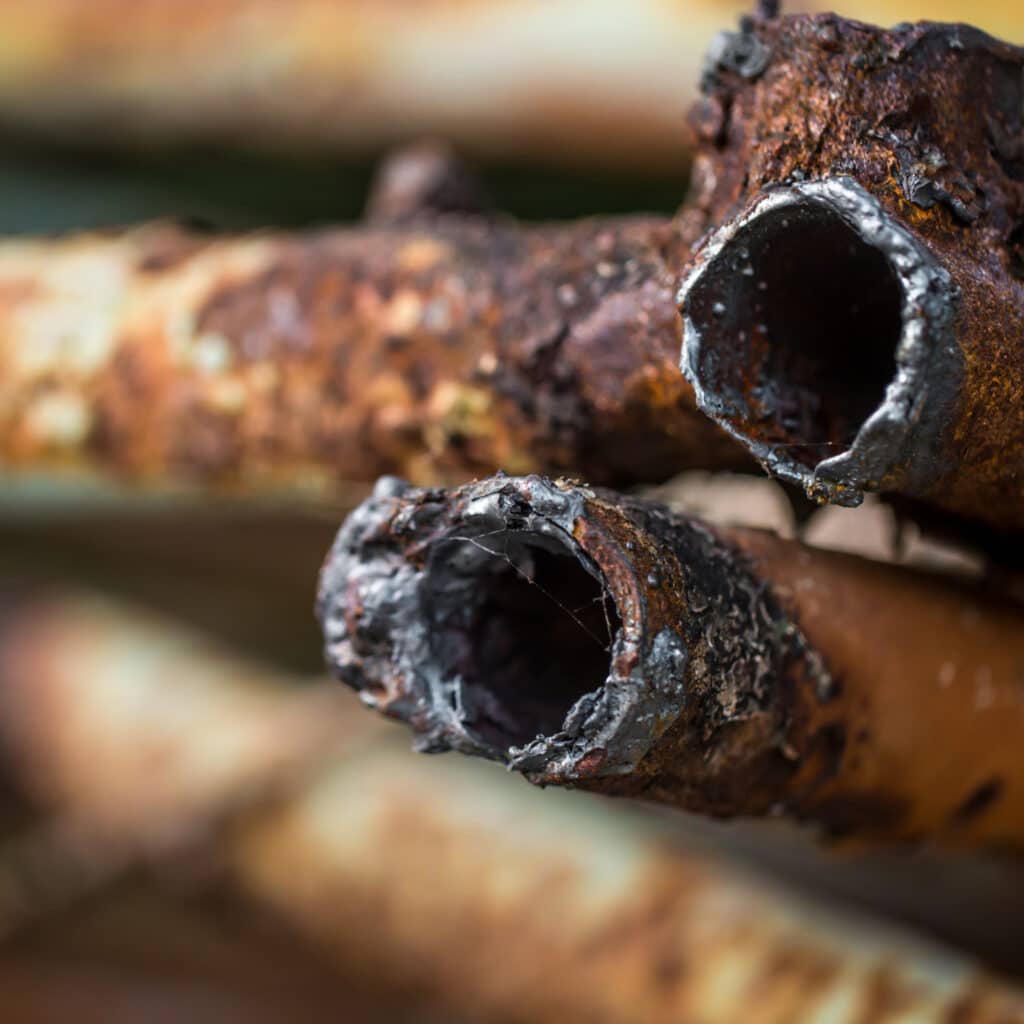
- Creep Fracture: This occurs when a material is exposed to continuous stress at elevated temperatures for a prolonged time. The material slowly deforms (creeps) and eventually fractures. It’s commonly seen in high-heat environments like turbine blades, boilers, and steam piping.
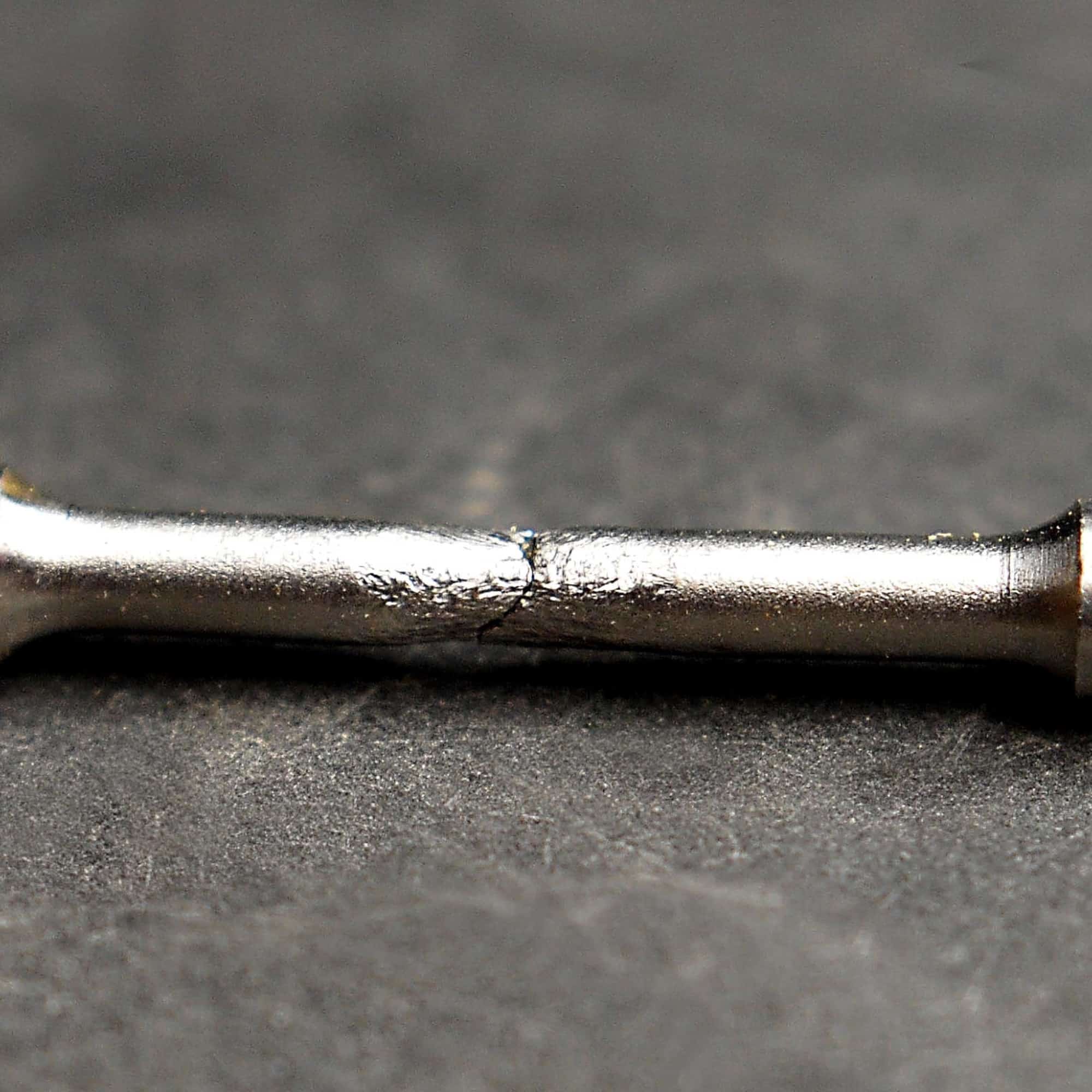
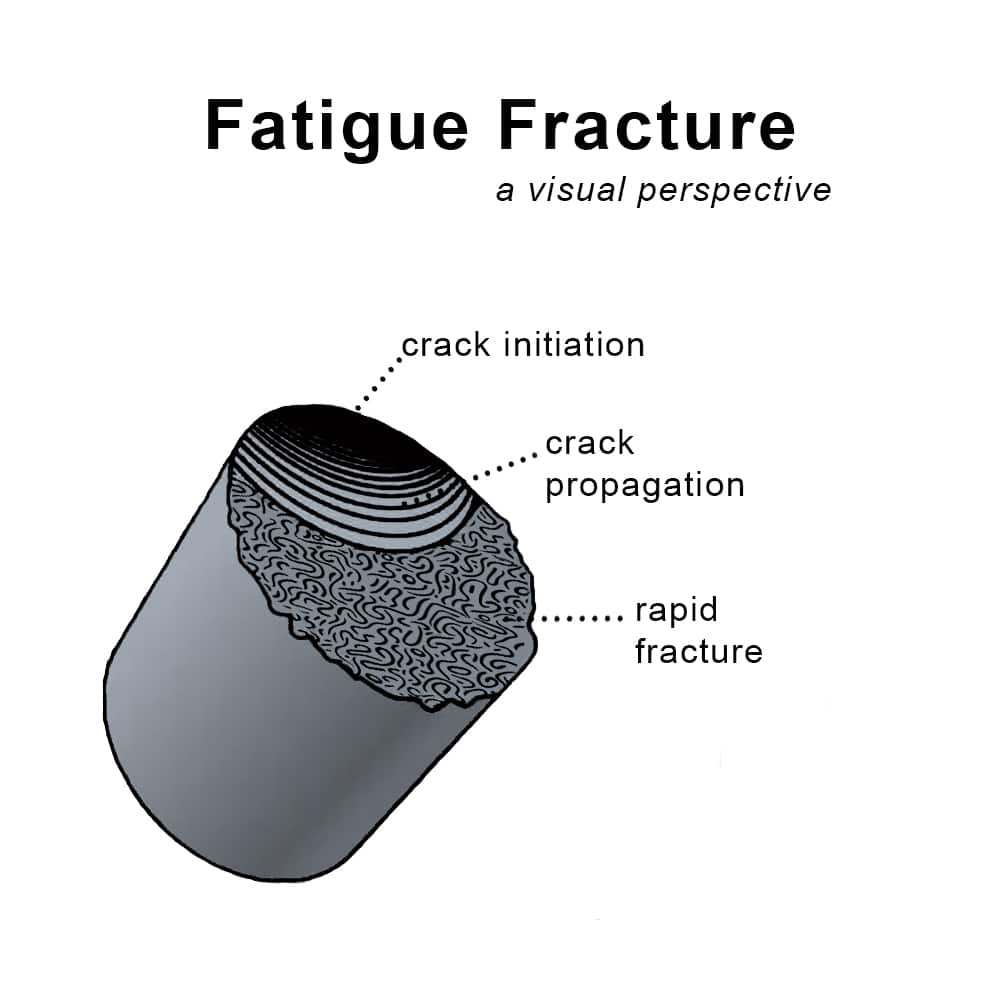
- Fatigue Fracture: Fatigue happens under repeated cyclic loading — even at stress levels well below the material’s yield strength. Over thousands or millions of cycles, microscopic cracks develop and gradually grow until the component fails. Aircraft structures, bridges, and rotating shafts are frequent fatigue-risk components.
Key distinction: Creep is driven by time, temperature, and constant stress, while fatigue is driven by fluctuating stresses and load cycles over time, usually at ambient or moderately elevated temperatures.